Quantitative trait loci
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support quantitative trait loci CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
A quantitative trait locus QTL is a region of DNA associated with a specific phenotype or trait that varies within a population. Typically, QTLs are associated with traits with continuous variance, such as height or skin color, rather than traits with discrete variance, such as hair or eye color. QTL mapping is a statistical analysis to identify which molecular markers lead to a quantitative change of a particular trait. Since a single locus may include many variants, imputation or whole-genome sequencing is a key prerequisite for QTL mapping to enable precise identification of the contributing molecular marker. QTLs have been expanded to include variants that act at different levels throughout the genotype-to-phenotype continuum. QTL analysis is an effective means of annotating variants that are associated with disease.
Quantitative trait loci
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Quantitative trait loci QTLs can be identified in several ways, but is there a definitive test of whether a candidate locus actually corresponds to a specific QTL? Much of the genetic variation that underlies disease susceptibility and morphology is complex and is governed by loci that have quantitative effects on the phenotype. Gene-gene and gene-environment interactions are common and make these loci difficult to analyse. This community mostly represents interests in the analyses of rodent quantitative trait loci QTLs , although many of the same principles apply to other species. With the development of new genetic techniques and with more information about the mammalian genome, we are confident that QTLs will become easier to identify and will provide valuable information about normal development and disease processes. At the first international meeting of the Complex Trait Consortium CTC box 1 in Memphis, Tennessee, United States May , the attendees decided that a document should be written to reflect the view of the community on the definition, mapping and identification of QTLs as a means to identify the molecular players that underlie complex phenotypes. Several distinct views have been presented in the literature on the definition and mapping of QTLs 1 - 7. In light of the controversies raised by some of these publications, the CTC held an open discussion of these issues through e-mail over an eight-month period see links in online links box. We intend these criteria to be sufficiently flexible and pragmatic to accommodate studies with a range of different scopes and objectives.
Pauwels, M. Previous work has shown that naive two-stage, vQTL screening-based interaction testing procedures can have inflated type I error whenever the exposure tested in stage two is associated with the outcome, quantitative trait loci to a correlation between test statistics for stage one and stage two
Our aim is to improve domesticated crop species by identifying useful genetic variation, and adapting this variation using conventional breeding techniques. The beneficial variation can be derived from 'exotic' allelic variants that are present in the wider species genepool, or, new combinations of beneficial genetic variation can be uncovered in our existing modern crop genepool. This type of variation is more amenable to being incorporated into our modern crop types, since in many cases it is already present in a close relative. Many of the characteristics that we wish to improve, such as, disease resistance, nitrogen use efficiency, post harvest quality, can be described as quantitative characteristics, since they display continuous variation and are relatively normally distributed in a population. The phenotype of a quantitative trait or characteristic is the cumulative result of many genes polygenes that may interact, are influenced to varying degrees by the environment, but together contribute towards the overall phenotype. By contrast, qualitative characteristics tend to be the result of the action of variants for a major gene. Classic examples are the Mendelian traits observed for pea seed shape wrinkled form versus smooth round and blood grouping in humans; these traits tend to place measurements into distinct classes.
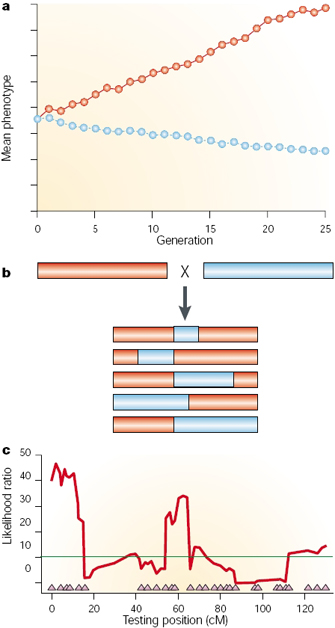
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. QTL analysis allows researchers in fields as diverse as agriculture, evolution , and medicine to link certain complex phenotypes to specific regions of chromosomes. The goal of this process is to identify the action, interaction , number, and precise location of these regions. In order to begin a QTL analysis, scientists require two things. First, they need two or more strains of organisms that differ genetically with regard to the trait of interest. For example, they might select lines fixed for different alleles influencing egg size one large and one small. Second, researchers also require genetic markers that distinguish between these parental lines.
Quantitative trait loci
The rules of inheritance discovered by Mendel depended on his wisely choosing traits that varied in a clear-cut, easily distinguishable, qualitative way. But humans are not either tall or short nor are they either heavy or light. Many traits differ in a continuous, quantitative way throughout a population. This histogram shows the distribution of heights among a group of male secondary-school seniors. As you can see, the plot resembles a bell-shaped curve. Such distributions are typical of quantitative traits.
Buck mason womens tees
There were also 71 ancestry-specific vQTLs reaching significance in one or more ancestry-specific analyses but not the meta-analysis Supplementary Data 4 , 61 of which were found in non-European-ancestry groups. It is important to remember that phenotypic variation can also be caused by environmental factors that are independent of genotype or through gene-environment interactions. For example, BACs that contain the candidate gene can be transfected into zygotes and the resulting mice can be tested for the quantitative trait. The genetics of species differences. Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Metabolite measurements were inverse-normal transformed prior to modeling. Retrieved 6 January Scientists dream of complex mice. Trends in Plant Science. Reprints and permissions. University of South Dakota School of Medicine. The dashed line represents the study-wide Bonferroni vQTL significance threshold. Much of the genetic variation that underlies disease susceptibility and morphology is complex and is governed by loci that have quantitative effects on the phenotype. Twenty metabolic biomarkers were pre-processed, including log transformation, adjustment for biological and technical covariates, and outlier removal.
Most of the phenotypic traits commonly used in introductory genetics are qualitative, meaning that the phenotype exists in only two or possibly a few more discrete, alternative forms, such as either purple or white flowers, or red or white eyes. These qualitative traits are therefore said to exhibit discrete variation. On the other hand, many interesting and important traits exhibit continuous variation ; these exhibit a continuous range of phenotypes that are usually measured quantitatively, such as intelligence, body mass, blood pressure in animals including humans , and yield, water use, or vitamin content in crops.
Examining anthropometric and lung function traits, they found a similar average number of vQTL relationships per effective phenotype 15 versus Darvasi, A. Genomic imprinting effects on adult body composition in mice. A QTL is a genetic locus, the alleles of which affect this variation. Unrelated individuals without major disease from any of four ancestry groups in the UK Biobank were included in the analysis. Overall, these permutation-based thresholds compare well with the Lander and Kruglyak threshold values, although the former tend to be less conservative. Because these strains are unlikely to contain segregating alleles of large effect at every locus contributing to variation in natural populations, some loci will remain undetected. What is meta QTL? The results of such an analysis are presented as a plot of the test statistic against the chromosomal map position, in recombination units cM. Save Cancel. The distribution of the effects of genes affecting quantitative traits in livestock.

Just that is necessary. I know, that together we can come to a right answer.
Something so is impossible