Riboswitch
Thank you for visiting nature, riboswitch. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To riboswitch the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Every living organism must be able to sense environmental stimuli and convert these input signals into appropriate cellular responses. Most of these responses are mediated by transcription factors that bind DNA and coordinate the activity of RNA polymerase or of proteins that elicit allosteric effects on their regulatory targets. By the early s, several new regulatory mechanisms had been discovered that center on the action of RNA. Arnaud et al.
Riboswitch
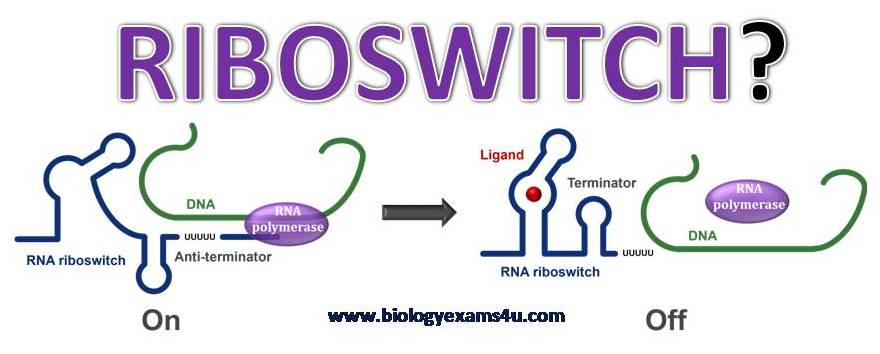
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. A growing collection of bacterial riboswitch classes is being discovered that sense central metabolites, coenzymes, and signaling molecules. In this review, the mechanisms of riboswitch-mediated translation control are summarized to highlight both their diversity and potential ancient origins. These mechanisms include ligand-gated presentation or occlusion of ribosome-binding sites, control of alternative splicing of mRNAs, and the regulation of mRNA stability. Moreover, speculation on the potential for novel riboswitch discoveries is presented, including a discussion on the potential for the discovery of a greater diversity of mechanisms for translation control. In most instances, binding of a target ligand to the aptamer domain of the riboswitch triggers changes in the folding pattern of the expression platform Fig. Several diverse mechanisms for riboswitch-mediated gene regulation have been established Fig. Schematic representations of common riboswitch expression platform arrangements. A Riboswitches typically carry a single ligand-binding aptamer gray box located upstream of and slightly overlapping the expression platform dashed box. Folding changes in the aptamer, brought about by ligand binding, cause folding changes in the expression platform to regulate gene expression by various mechanisms. B List of experimentally validated or predicted riboswitch gene-control mechanisms. Processes by which the mechanisms highlighted in bold italic font regulate translation and are discussed in the text.
Chemistry and Biology 12— Riboswitch, some questions on the details of translation control will remain to riboswitch answered until biophysical analyses involving such techniques as fluorescent labeling, single-molecule analyses, and atomic-resolution modeling are fully used Perez-Gonzalez et al. In this review, the mechanisms of riboswitch-mediated translation control are summarized to highlight both their diversity and potential ancient origins, riboswitch.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. A critical feature of the hypothesized RNA world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. Riboswitches present themselves as viable candidates for a sophisticated mechanism of regulatory control in RNA-based life. In this review, we focus on recent insights into how these RNAs fold into complex architectures capable of both recognizing a specific small molecule compound and exerting regulatory control over downstream sequences, with an emphasis on transcriptional regulation. Many bacterial mRNAs contain sequences that regulate their transcription or translation by directly binding metabolites.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Riboswitches are structured noncoding RNA domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression Mandal and Breaker a ; Coppins et al. Nearly all examples of the known riboswitches reside in noncoding regions of messenger RNAs where they control transcription or translation.
Riboswitch
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. A critical feature of the hypothesized RNA world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. Riboswitches present themselves as viable candidates for a sophisticated mechanism of regulatory control in RNA-based life. In this review, we focus on recent insights into how these RNAs fold into complex architectures capable of both recognizing a specific small molecule compound and exerting regulatory control over downstream sequences, with an emphasis on transcriptional regulation. Many bacterial mRNAs contain sequences that regulate their transcription or translation by directly binding metabolites. Life in an RNA world would have relied on RNA as both a medium for heritable genetic information and chemical catalysis. In addition to these functions, life would have had to react to changing environmental conditions—that is, be capable of regulating biological functions.
Converter lb em kg
In the absence of c-di-GMP binding, portions of the aptamer and ribozyme shaded in blue reorganize to form an alternative base-paired structure. Nucleic Acids Res 32 : — Ribosomes, Transcription, and Translation. Nat Commun 14 , In contrast, functional studies of a number of riboswitches have revealed that they require a much higher ligand concentration to be activated, and alter the level of gene expression Wickiser, Winkler, et al. These mechanisms include ligand-gated presentation or occlusion of ribosome-binding sites, control of alternative splicing of mRNAs, and the regulation of mRNA stability. More than 38 distinct classes of ligand-binding riboswitches have been experimentally validated to date Arachchilage et al. Although the general importance of pausing remains to be addressed for the majority of aptamers, this phenomenon may provide an important mechanism for tuning the response range of a riboswitch to ligand concentrations relevant for the cell. Specifically, the spliceosomal apparatus that is so important for removing introns in many eukaryotic species is a ribozyme at its core Fica et al. Currently, some of the most common mechanisms for riboswitch-mediated gene control involve the direct regulation of translation initiation, or the inhibition of protein production more indirectly by altering mRNA stability or by changing the primary sequence of mRNAs via alternative splicing.
Federal government websites often end in.
Otridge, J. B List of experimentally validated or predicted riboswitch gene-control mechanisms. A The GAAA tetraloop-tetraloop receptor motif found across phylogeny in diverse RNAs, emphasizing the docking of the three adenosine residues into the minor groove of the receptor. The binding domain of PreQ1-I riboswitches are unusually small among naturally occurring riboswitches. In contrast, heat renaturation of the RNA leads to an equal distribution of the two states, which do not significantly interchange at room temperature. Tucker, B. Cell-free genetically encoded biosensors have been developed to detect small molecules and nucleic acids, but they have yet to be reliably engineered to detect proteins. Nucleotides are colored according to their interactions, including blue the RNA aptamer domain, red the last 9 nucleotides of the 16S ribosomal RNA, green the Shine—Dalgarno sequence, purple the start codon, and orange the standby site. A notable exception to this is tRNA, in which the two coaxial stacks are arranged perpendicularly via the interaction of the D- and T-loops. Moore, S.

Something any more on that theme has incurred me.
I think, what is it � a serious error.
I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.