Sas if then statement
An if-then statement can be used to create a new variable for a selected subset of the observations. For each observation in the data set, SAS evaluates the expression following the if.
Again, once you've read your data into a SAS data set, you probably want to do something with it. A common thing to do is to change the original data in some way in an attempt to answer a research question of interest to you. In the last lesson, we learned how to use assignment statements and functions to add some information to all of the observations in the data set. In this lesson, we will learn how to use if-then-else statements to add some information to some but not all of the observations in your data set. In this lesson, we investigate a number of examples that illustrate how to change a subset of the observations in our data set.
Sas if then statement
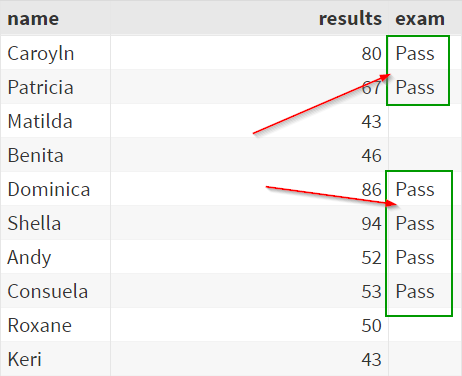
The ELSE statement is optional. It can be used to execute a statement if the condition is not true. Sometimes, we might need to execute more than one statement when the condition is met. Sign In. Members' area. Master SAS in 30 days! Start Your Free Training Now. The data set above contains 10 students and their exam results. DO Group. The DO group starts with the DO statement. Do you have a hard time learning SAS? Start Course for Free!
DO Group.
Continues processing only those observations that meet the condition of the specified expression. The subsetting IF statement causes the DATA step to continue processing only those raw data records or those observations from a SAS data set that meet the condition of the expression that is specified in the IF statement. If the expression is true for the observation its value is neither 0 nor missing , SAS continues to execute the DATA step and includes the observation in the output data set. If the expression is false its value is 0 or missing , no further statements are processed for that observation or record, the current observation is not written to the data set, and the remaining program statements in the DATA step are not executed. SAS immediately returns to the beginning of the DATA step because the subsetting IF statement does not require additional statements to stop processing observations. This matches patterns that occur at the beginning of a string.
The following examples show how to use each of these statements in practice with the following dataset in SAS:. The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SAS:. January 17, January 12, January 18, How to Add Target Line to Graph in How to Convert Date of Birth to Age
Sas if then statement
Executes a statement for rows that meet specific conditions. Overview of Statements. Block Statements. Global Declaration Statements. Local Statements. Assignment Statement.
Fairy tail cana wallpaper
By the way, when making comparisons that involve character values, you should know that SAS considers a missing character value a blank space ' ' to be smaller than any letter, and so the good habit of programming for missing values holds when dealing with character variables as well. It's just a matter of preference. Master SAS in 30 days! Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. Suppose she wants to add two points to a student's overall average if either her first exam grade is less than her third and fourth exam grade or her second exam grade is less than her third and fourth exam grade. Now when we look at examples using these logical operators, why stop at just two ELSE statements? Inline Feedbacks. PUT: Column. Again, when comparisons are connected by AND, all of the comparisons must be true in order for the condition to be true. When the expression is false, SAS ignores the statement following then. IN Operator IN operator is used to select multiple values of a variable.
The expression is true if a non-zero or non-missing result is generated.
As the output from Example 5. Is the instructor treating the glass as being half-full as opposed to half-empty? At end only else how it works? This matches patterns that occur at the beginning of a string. What went wrong? PUT: Formatted. Creating New Variables Using if-then ; if-then-else ; and if-then-else-then Statements An if-then statement can be used to create a new variable for a selected subset of the observations. Review the output from the PRINT procedure to convince yourself that this time the values of the character variable status really have been assigned correctly. Note that this program also illustrates the use of more than one ELSE statement. There is nothing really new here. Start Course for Free! If you try it, you'll soon learn that SAS will hiccup at you. You may have noticed, after the condition that takes care of missing values, that the conditions appear in order from A, B, First, inspect the program to make sure you understand the code. And, you will want to use the NOT operator in conjunction with other operators to reverse the logic of a comparison:.

Absurdity what that
You commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.