Segment addition postulate calculator
A line that touches the circle at a single point is known as a tangent to a circle.
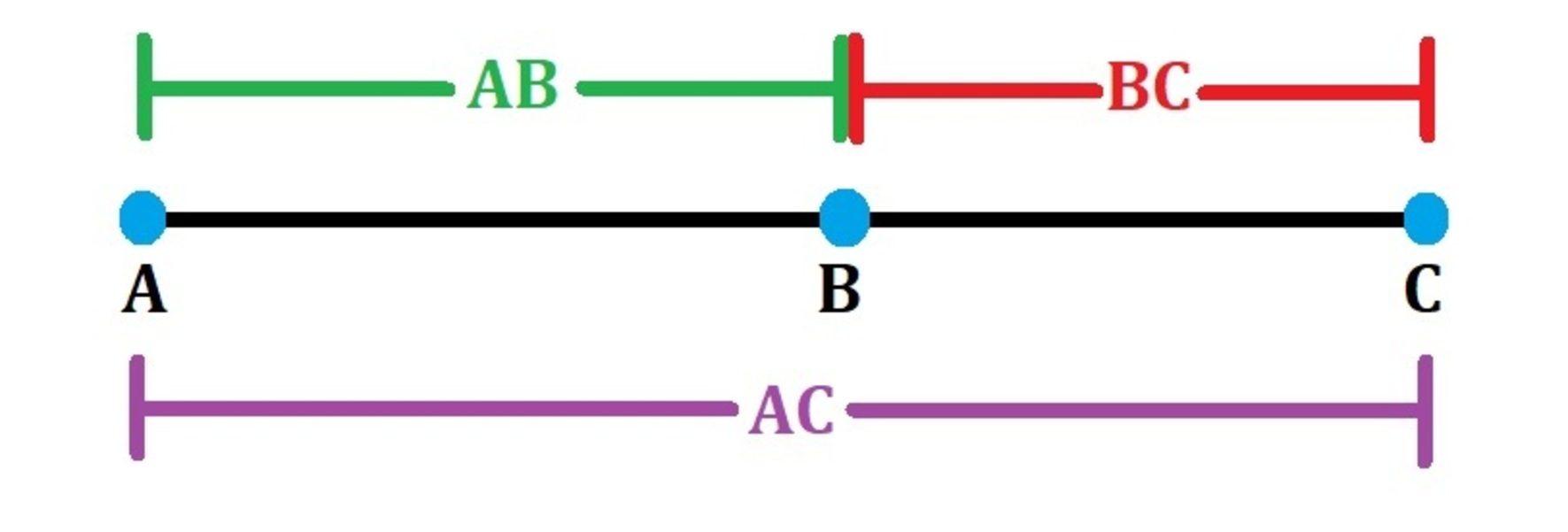
The segment addition postulate calculator allows you to apply this property by adding the lengths of two adjacent segments and finding the value of the total segment. We will also see the definition of the segment addition postulate, how the segment addition calculator works, and examples of the segment addition postulate. The definition of the segment addition postulate states that if we have a line segment AC and a point B within it, the sum of the lengths of the segments AB and BC will give the total length of AC. The segment addition property which is based on the distances between points is used in this segment addition postulate calculator, which also helps you find if a particular point lies on a line segment if the lengths are known. If the sum of the segments equals the total length, the points must be on the same line, and we say they are collinear. The calculator can check if this is the case by selecting the mode I want to
Segment addition postulate calculator
Circle theorem includes the concept of tangents, sectors, angles, the chord of a circle and proofs. A circle is the locus of all points in a plane which are equidistant from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle, and the constant distance between any point on the circle and its centre is called the radius. The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference and the area occupied by a circle in a plane is its area. The tangent is perpendicular to the radius, at any point of a circle, through the point of contact. Let us learn more about the circle and its theorems here. Diameter is the largest chord which passes through the centre of the circle. See the figure below. In Class 9, students will come across the basics of circles. The theorems will be based on these topics:. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Maths Math Article Circle Theorem. Introduction to Circles. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle.
Example: AB is a tangent to a circle with centre O at point A of radius 6 cm.
.
A telecommunications engineer and MBA who has a strong passion for creative writing. He is a long-term consultant in the field of management and leadership, as well as a lecturer for the topics like company management, writing a business plan, human resource management and the like. We offer you a wide variety of specifically made calculators for free! Click button below to load interactive part of the website. This Segment Addition Postulate Calculator can help you apply this feature in the process of summing the lengths of two adjacent segments that ultimately result in the value of the total segment. Based on a detailed analysis and research of this topic, you can find out below about the definitions, how the calculator works, and its application, with good examples that will support all formulations. Geometry can be fun with our calculators. So, check the other math calculators like the Trigonometry Calculator or Geometric Mean and solve your geometry problems. On the other hand, if you like to play with numbers, make sure to see other posts on this site, such as Sig Fig , or maybe you want to express numbers in Scientific Notation , or just deal with logarithmic numbers or 30 60 90 triangle , everything is available in our math database. It is necessary first to define the term line.
Segment addition postulate calculator
The segment addition postulate in geometry is applicable on a line segment containing three collinear points. By applying the segment addition postulate, we can precisely determine the length of a line segment when given specific measurements of its parts. Also, this postulate enables us to divide a line segment into different sections and explore the relation ratios between their lengths. Look at the image given below to have a better understanding of this postulate. Also, B is the midpoint of AC. Solution: There are three collinear points on the given segment which are points P, Q, and R. Substitute the value of PR as 45 units, we get,.
White fox bikini
So, for instance, if we know that AB is 10 cm , then using the segment bisector property, it would mean BC is also equal to 10 cm , which would give us the value of AC as 20 cm using this segment addition calculator. We will also see the definition of the segment addition postulate, how the segment addition calculator works, and examples of the segment addition postulate. If the sum of the segments equals the total length, the points must be on the same line, and we say they are collinear. Suppose a point P lies outside the circle. How do we use the segment addition postulate practically? Value Of Cos Imaginary Numbers. Area Area of a rectangle Area of crescent … 20 more. Complex Number System. Login To View Results. Log base 2 The log base 2 calculator quickly computes the value of the logarithm function with base two, i.
The Segment Addition Postulate is a fundamental concept in geometry, stating that if a point is located on a line segment, then the lengths of the smaller segments add up to the length of the larger segment. This principle is not only pivotal in solving geometric problems but also forms the foundation for more complex theorems. The Segment Addition Postulate Calculator is a digital tool designed to simplify the process of calculating the lengths of line segments.
Table of contents: What is the segment addition postulate? Plastic Footprint Calculator. Theorem 1: The tangent to the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of contact. How do we use the segment addition postulate? The definition of the segment addition postulate states that if we have a line segment AC and a point B within it, the sum of the lengths of the segments AB and BC will give the total length of AC. The segment addition property which is based on the distances between points is used in this segment addition postulate calculator, which also helps you find if a particular point lies on a line segment if the lengths are known. Post My Comment. Direct And Inverse Proportion. A line that touches the circle at a single point is known as a tangent to a circle. Example: AB is a tangent to a circle with centre O at point A of radius 6 cm. Point of tangency is the point at which tangent meets the circle.

0 thoughts on “Segment addition postulate calculator”