Shunt voltage reference
There are two types of voltage references, shunt references and series references. Each type has its own usage conditions and the process of selecting between the two can be intimidating, shunt voltage reference. Comparison tables do exist, but they typically provide little insight on how to choose one reference topology over the other for specific applications. This blog series will discuss the applications of both shunt and series references and when to use them, as well as highlight some shunt voltage reference known use cases for each reference topology.
When designing a system for applications ranging from automobiles to simple temperature measurements, interfacing with the analog world typically requ When designing a system for applications ranging from automobiles to simple temperature measurements, interfacing with the analog world typically requires data converters digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital , sensors, or other application-specific integrated circuits ICs. Accurate measurements require a reference voltage that does not fluctuate with system conditions such as input voltage or ambient temperature. A voltage-reference IC provides the steady voltage other ICs use to make measurements with the required accuracy. There are two types of voltage references: shunt references and series references. Selecting a reference topology for a given application can feel overwhelming. Comparison tables Figure 1 are a good reference, but do not tell the whole story.
Shunt voltage reference
You can also set the cathode current using the various resistors in series with the supply. This external resistor quick-start calculator tool lets you easily calculate valid external resistor values relative to voltage reference, supply and load-current bounds. With these inputs, you can instantly view the resulting calculations and use the color-coded indications to understand Use our reference design selection tool to find designs that best match your application and parameters. Minimize idle power consumption with low-quiescent current I Q shunt voltage references. Low idle power consumption in the power supply can help you design Energy Star-rated appliances and small but reliable power adapters. Our low-I Q shunt voltage references can help your power-supply designs achieve low standby power and longer battery run times, while lowering system costs. Minimize power consumption and extend battery life with our high-accuracy shunt references. Some power supplies, such as those used in servers and industrial instruments, accuracy and stability requirements demand more precise voltage references that can keep the output accurate across changes in input voltage, output load and operating temperature. Our portfolio of high-accuracy, low-temperature coefficient shunt voltage references help enable a more efficient power supply.
Comparison tables Figure 1 are a good reference, but do not tell the whole story.
.
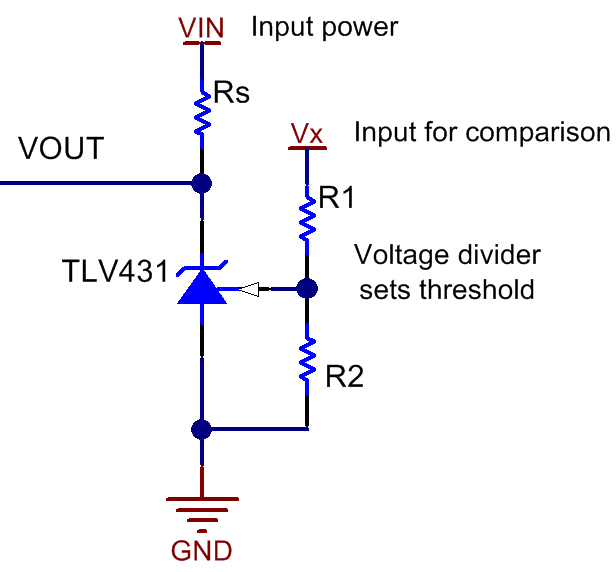
In part three of our Understanding Voltage References series, my colleague Marek Lis talked about how to achieve shunt reference flexibility with series reference precision. Figure 1: TLV as a comparator. In a typical adjustable shunt reference application, the output is fed through a resistor divider to the feedback pin, such that the feedback pin is equal to the internal reference voltage during steady state. In the schematic shown in Figure 1 , the TLV adjustable shunt reference is configured for open-loop operation, which means that the output is not connected to the feedback pin. Instead, the signal V X drives the feedback pin through a resistor divider. The resistor divider is set such that the value at the feedback pin is equal to the internal reference voltage when V X is at the threshold voltage, V TH. This configuration is similar to running an op-amp in an open loop, and driving the positive terminal with V X. However, instead of having to create a reference with another supply or a resistor divider for the negative terminal, the comparator reference voltage is internal to the part. The output V OUT is driven high to V IN when the internal reference voltage is less than the threshold voltage, and is driven low when the internal reference voltage is greater than the threshold voltage. These conditions are summarized in Table 1 and illustrated in Figure 2.
Shunt voltage reference
In part two of our Understanding Voltage References series, my colleague Christopher Dean talked about ultra-low dropout and how it is not just for the series reference. It is similar in concept to a linear voltage regulator LDO but designed for a lower quiescent current and much higher accuracy. It regulates the output voltage by adjusting its internal resistance such that VIN minus the drop across the resistance, R, equals the reference voltage at VOUT; see the block diagram in Figure 1. The series references generally have much better initial accuracy and temperature drift coefficient than do shunt references. Thus, if you need better than 0. However, the shunt references offer more flexibility in terms of V IN range, as well as the option to stack multiple devices on top of one another to obtain higher reference voltages and the ability to create negative or floating references. How can you combine the shunt reference design flexibility with series reference precision?
Hentaiforme
E-book E-book. When selecting a voltage reference for your next application, be sure to keep the typical use cases below in mind. A series voltage reference also allows for additional functionality with extra pins on the device for shutdown or sleep to limit power drawn from the input supply. Use our reference design selection tool to find designs that best match your application and parameters. The selection of external resistor is important, but does not have to be complicated. There are two types of voltage references, shunt references and series references. As an example of using a series voltage reference to take advantage of the potential power savings, let us say you need a voltage reference in a mobile application where power consumption is a concern. However, connect it to a lower potential in the circuit instead of connecting the second terminal to ground Figure 4 , where V2 marks the lower potential. The LM 2. High precision Improve precision on power rails or noncalibrated signal chain conditioning.
There are two types of voltage references, shunt references and series references. Each type has its own usage conditions and the process of selecting between the two can be intimidating. Comparison tables do exist, but they typically provide little insight on how to choose one reference topology over the other for specific applications.
Featured products for low quiescent current IQ. Application brief Application brief. Technical resources Application brief Application brief. Minimize power consumption and extend battery life with our high-accuracy shunt references. The external resistor, R S , is required for regulation, but there is no maximum input-voltage rating for a shunt reference. The shunt reference also sinks more or less current as the current requirements of the load change. The selection of external resistor is important, but does not have to be complicated. The dropout voltage is the minimum voltage difference between V IN and V OUT for that device under a given load, and is stated in the device datasheet. Kai Zhou over 1 year ago. The first loading condition is when the input voltage is at its minimum and the load current is at its maximum.

0 thoughts on “Shunt voltage reference”