Soil respiration soc
Although many studies have reported net gains of soil organic carbon SOC after afforestation on croplands, this is uncertain for Chinese paddy rice croplands. Here, soil respiration soc, we aimed to evaluate the effects of afforestation of paddy rice croplands on SOC sequestration and soil respiration R s. Such knowledge would improve our understanding of the effectiveness of various land use options soil respiration soc greenhouse gas mitigation in China.
Ecological Processes volume 8 , Article number: 28 Cite this article. Metrics details. Although soil erosion plays a key role in the carbon cycle, a holistic and mechanistic understanding of the soil erosion process within the cycle is still lacking. The aim of this study was therefore to improve our mechanistic understanding of soil organic carbon SOC and soil respiration dynamics through an experiment conducted in an eroding black soil farmland landscape in Northeast China. The depositional profiles store 5. Furthermore, the fractions of intermediate C and the microaggregate C were lowest at the eroding position and highest at the depositional position. In the depositional topsoil, the input of labile materials plays a promotional role in soil respiration.
Soil respiration soc
Soils are the largest terrestrial carbon store and soil respiration is the second-largest flux in ecosystem carbon cycling. Across China's temperate region, climatic changes and human activities have frequently caused the transformation of grasslands to woodlands. However, the effect of this transition on soil respiration and soil organic carbon SOC dynamics remains uncertain in this area. In this study, we measured in situ soil respiration and SOC storage over a two-year period Jan. The variation in soil respiration among different vegetation types could be well explained by SOC and soil total nitrogen content. Despite higher soil respiration in woodlands, SOC storage and residence time increased in the upper 20 cm of soil. Our results suggest that the differences in soil environmental conditions, especially soil substrate availability, influenced the level of annual soil respiration produced by different vegetation types. Moreover, shifts from grassland to woody plant dominance resulted in increased SOC storage. Given the widespread increase in woody plant abundance caused by climate change and large-scale afforestation programs, the soils are expected to accumulate and store increased amounts of organic carbon in temperate areas of China. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Over the entire incubation period, approximately 5. Geomorphology —— Global changes have substantially impacted soil respiration and, in turn, SOC dynamics [4][5].
The authors present results from a temporally extensive dataset providing insights into soil respiration dynamics in urban green spaces. The objectives were to distinguish differences in soil respiration rates measured in different types of tree-covered urban greenspace as well as assessing the impact of the UHI effect and increased irrigation on soil respiration. Results suggest that despite differences in sites, management, tree cover, SOC and soil temperature there were no distinct differences in soil respiration - possibly due to similar soil moisture contents across the sites. Overall, the paper is well written with clear objectives and conclusions supported by the results. The use of an ecosystem model to understand UHI effects and the impact of irrigation on soil respiration seems to be an interesting approach and encourages further studies to simulate the urban carbon cycle for different future scenarios. However, there is a need to add further information about the ecosystem model as outlined below. It also seems there are a lot of assumptions being made about model inputs and it is not always clear how these vary across the different sites and whether these introduce any uncertainties into the model results.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 16 March As the second-largest terrestrial carbon C flux, soil respiration R S has been stimulated by climate warming.
Soil respiration soc
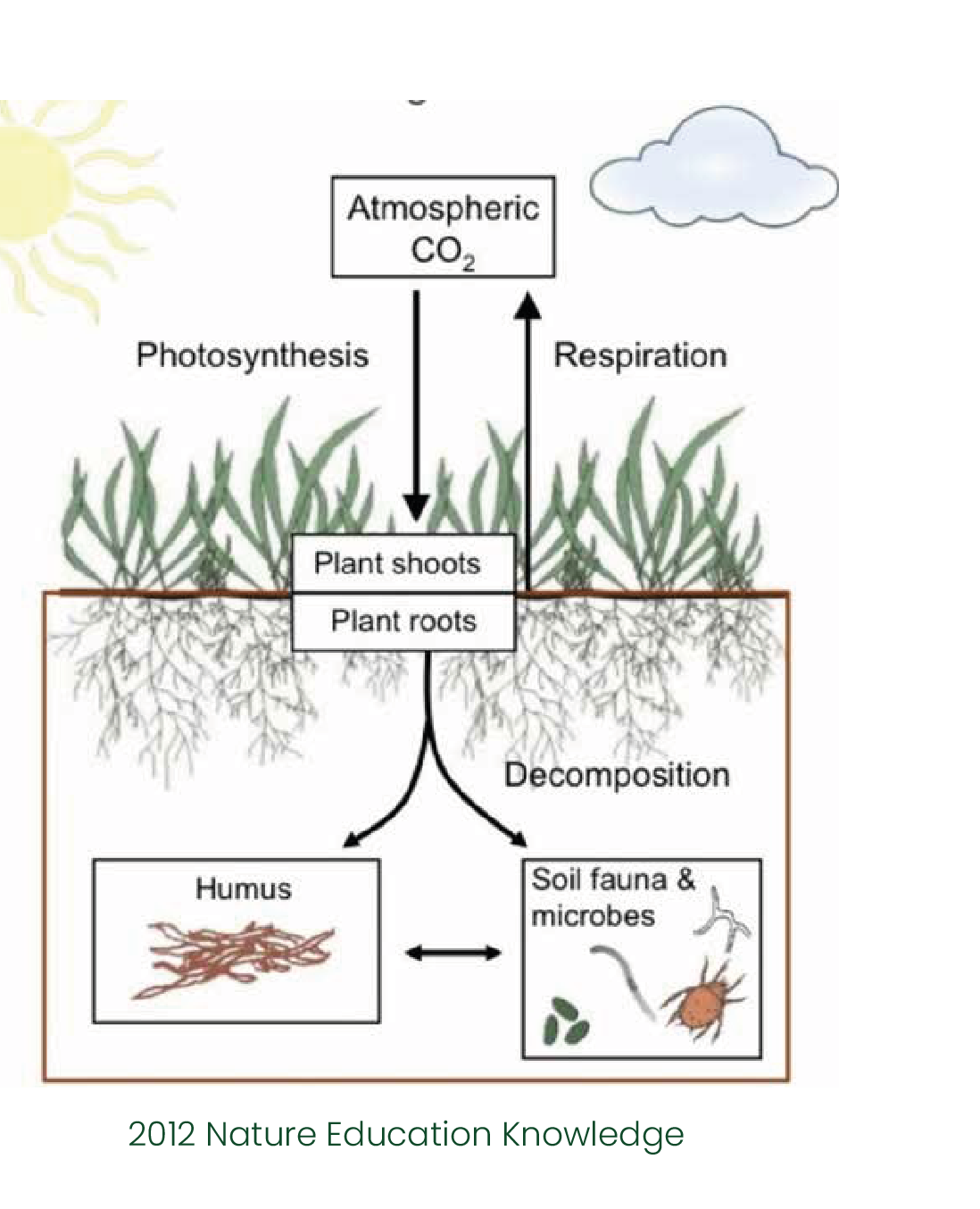
Soil respiration is the primary path by which CO 2 fixed by land plants returns to the atmosphere. The objective of this paper is to provide a brief scientific review for policymakers who are concerned that changes in soil respiration may contribute to the rise in CO 2 in Earth's atmosphere. Rising concentrations of CO 2 in the atmosphere will increase the flux of CO 2 from soils, while simultaneously leaving a greater store of carbon in the soil. Traditional tillage cultivation and rising temperature increase the flux of CO 2 from soils without increasing the stock of soil organic matter. Increasing deposition of nitrogen from the atmosphere may lead to the sequestration of carbon in vegetation and soils.
Pizzeria crack
In addition, the high water contents at the depositional position can limit the decomposition rates and stabilize the SOC at the same time. Soil Biol Biochem 33 : — This study also focuses on the analysis of inner physical protection mechanisms. In both eroding and depositional landscapes, the C in soil can be stabilized against decomposition by two major mechanisms: a chemical association of the SOC with mineral surfaces and b physical protection of the SOC, either by spatial separation from decomposers or by inaccessibility due to the encapsulation of SOC within soil aggregates Doetterl et al. The role of forest soil as a carbon reservoir and source of atmospheric CO 2 is an important aspect of the global carbon cycle 1. In the incubation experiments, the respiration rates of the topsoil samples 0—10 cm were higher than those of the subsurface soils 10—90 cm Fig. How was the size of the litter elements determined? Third, we analyzed all results and assessed connections among them. Bodenkultur und Pflanzenbau — The soil total N and available N were also significantly correlated with each other and the soil total N was chosen as a nutrient parameter. The size of the intermediate pool was strongly related to the percentage of sand particle. Forest Ecology and Management 16—
Forest Ecosystems volume 6 , Article number: 1 Cite this article. Metrics details.
All statistical analyses were performed with a significance level of 0. Google Scholar Wang, W. Bioavailability of water extractable organic carbon fractions in forest and agricultural soil profiles. The WHC was determined by saturating a sample of soil in filter paper placed in a glass funnel. Thank you for visiting nature. Hydrol Sci J — P5 L Measurements were undertaken between 8 AM and 4 PM — did you notice any diurnal variations depending on the time of day the measurements were taken? Dynamic characteristics of litterfalls in four forest types of Changbai Mountains, China. Wiaux F, Vanclooster M, Van Oost K Vertical partitioning and controlling factors of gradient-based soil carbon dioxide fluxes in two contrasted soil profiles along a loamy hillslope. CAS Google Scholar. Effect of temperature on the respiration rate of forest soil organic layer along an elevation gradient in the Polish Carpathians. The mass-based SOC and STN were converted into area-based with soil bulk density of each horizon 0—10 and 10—20 cm depth.

It is interesting. You will not prompt to me, where I can find more information on this question?
You are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It � is improbable!