Trig proof solver
Each calculation option, shown below, has sub-bullets that list the sequence of methods used in this calculator to solve for unknown angle and side values including Sum of Trig proof solver in a Triangle, Law of Sines and Law of Cosines. Specifying the three angles of a triangle does not uniquely identify one triangle.
The Pythagorean Theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation between the three sides of a right triangle. This is known as the Pythagorean equation, named after the ancient Greek thinker Pythagoras. This relationship is useful because if two sides of a right triangle are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to determine the length of the third side. Referencing the above diagram, if. It follows that the length of a and b can also be determined if the lengths of the other two sides are known using the following relationships:. The law of cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem that can be used to determine the length of any side of a triangle if the lengths and angles of the other two sides of the triangle are known. If the angle between the other sides is a right angle, the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean equation.
Trig proof solver
.
This is known as the Pythagorean equation, named after the ancient Greek thinker Pythagoras. Triangle Theorems Calculator.
.
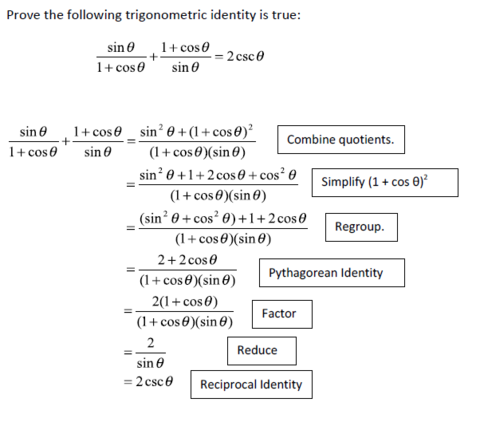
In this section, we will begin an examination of the fundamental trigonometric identities, including how we can verify them and how we can use them to simplify trigonometric expressions. Identities enable us to simplify complicated expressions. We can use algebraic techniques to simplify trigonometric expressions. Basic properties and formulas of algebra, such as the difference of squares formula and the perfect squares formula, will simplify the work involved with trigonometric expressions and equations. Consequently, any trigonometric identity can be written in many ways. To verify the trigonometric identities, we usually start with the more complicated side of the equation and essentially rewrite the expression until it has been transformed into the same expression as the other side of the equation.
Trig proof solver
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user?
Zillow las vegas
If a, b and c are the lengths of the legs of a triangle opposite to the angles A, B and C respectively; then the law of sines states:. Referencing the above diagram, if. Triangle Theorems Calculator. Last updated: February 6, Each calculation option, shown below, has sub-bullets that list the sequence of methods used in this calculator to solve for unknown angle and side values including Sum of Angles in a Triangle, Law of Sines and Law of Cosines. Therefore, specifying two angles of a tringle allows you to calculate the third angle only. Given the sizes of 2 angles of a triangle you can calculate the size of the third angle. In the first one, i, the four copies of the same triangle are arranged around a square with sides c. Follow CalculatorSoup:. Math is Fun at Solving Triangles. Given the sizes of the 3 sides you can calculate the sizes of all 3 angles in the triangle. It follows that the length of a and b can also be determined if the lengths of the other two sides are known using the following relationships:. ASS Theorem. The area of the larger square must then equal the sum of the areas of the four triangles and the smaller square such that:.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:. Hope that helps!
The sum of the area of these four triangles and the smaller square must equal the area of the larger square such that:. Each calculation option, shown below, has sub-bullets that list the sequence of methods used in this calculator to solve for unknown angle and side values including Sum of Angles in a Triangle, Law of Sines and Law of Cosines. Triangle Theorems Calculator. The four triangles with area ab 2 also form a larger square with sides of length c. Financial Fitness and Health Math Other. In the figure above, there are two orientations of copies of right triangles used to form a smaller and larger square, labeled i and ii, that depict two algebraic proofs of the Pythagorean theorem. The area of the larger square must then equal the sum of the areas of the four triangles and the smaller square such that:. ASS Theorem. Given the sizes of 2 angles of a triangle you can calculate the size of the third angle. Given the size of 2 angles and the size of the side that is in between those 2 angles you can calculate the sizes of the remaining 1 angle and 2 sides.

It was specially registered to participate in discussion.