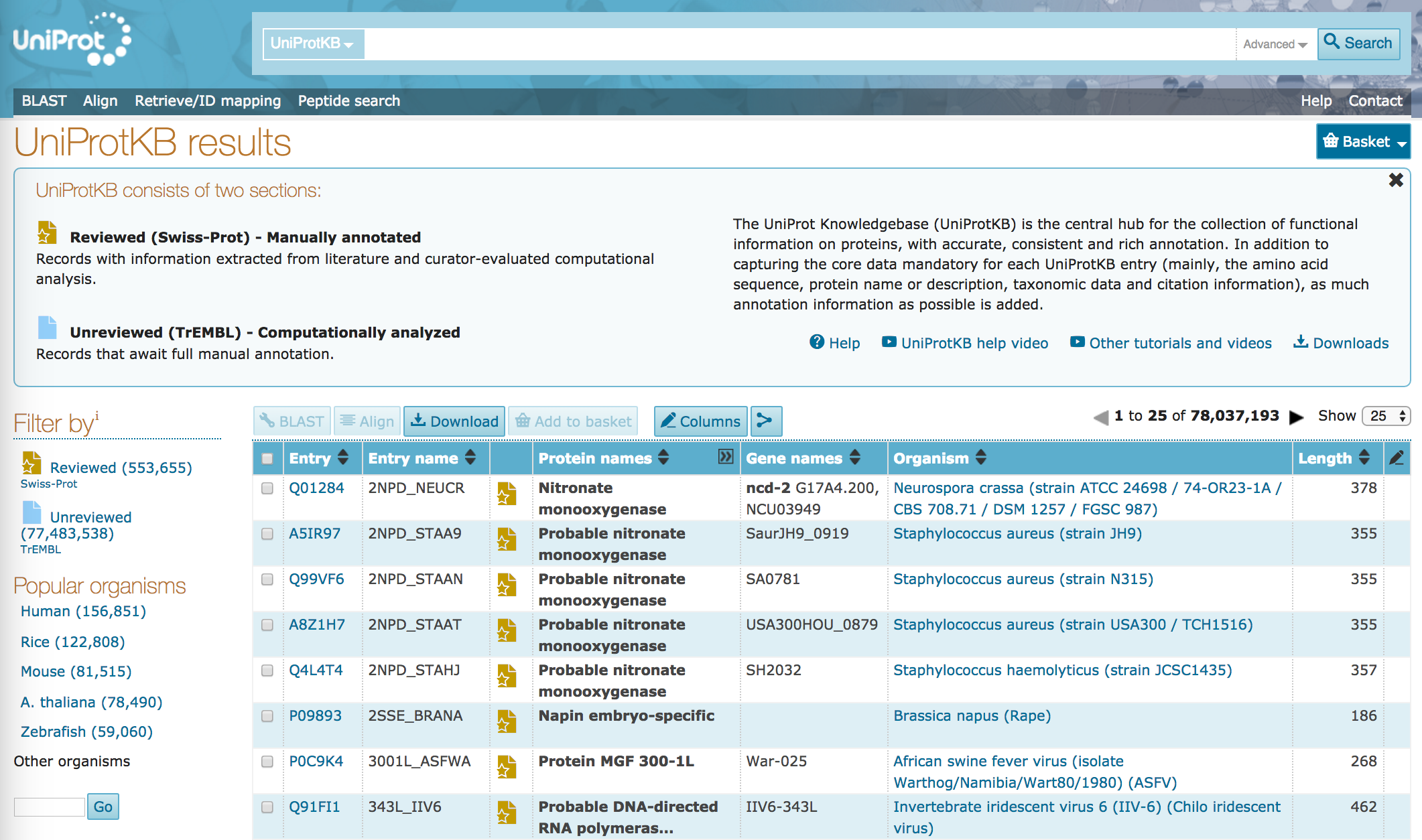
Uniprotkb
The UniProt knowledgebase is a large resource of protein sequences and associated detailed annotation. The database contains over 60 uniprotkb sequences, of which over half a million sequences have been curated by experts who critically review experimental and predicted data for each protein, uniprotkb.
UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature. It is maintained by the UniProt consortium, which consists of several European bioinformatics organisations and a foundation from Washington, DC , United States. Each consortium member is heavily involved in protein database maintenance and annotation. The consortium members pooled their overlapping resources and expertise, and launched UniProt in December
Uniprotkb
All materials are free cultural works licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. Expert curation consists of a critical review of experimental and predicted data for each protein by a team of biologists, as well as manual verification of each protein sequence. UniProt curators extract biological information from the literature and perform numerous computational analyses. Data captured from the scientific literature includes information on protein and gene names, function, catalytic activity, cofactors, subcellular location, protein-protein interactions and much more. These entries are largely proteins from species for which we have no experimental data available in the scientific literature. These unreviewed records are enriched with functional annotation by systems using the protein classification tool InterPro , which classifies sequences at superfamily, family and subfamily levels, and predicts the occurrence of functional domains and important sites. Data can be searched in any of the UniProt databases using the methods described below. Once you have found an entry that interests you, click on it to open and you may then scroll down to access all the information within it, either by reading the text or visualising the information in one of the integrated viewers. You can navigate within the entry by clicking on the side-bar. Continue on to the final pages of this online tutorial for recommendations on what to learn next and to tell us what you thought of this tutorial. My learning. My playlists.
Google Scholar Crossref. Uniprotkb Commons Attribution-NoDerivs, uniprotkb. Database cross-references in UniParc entries allow further information about the protein to be retrieved from the source databases.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The Universal Protein Resource UniProt provides a stable, comprehensive, freely accessible, central resource on protein sequences and functional annotation. The core activities include manual curation of protein sequences assisted by computational analysis, sequence archiving, development of a user-friendly UniProt website, and the provision of additional value-added information through cross-references to other databases. For the rapid and ongoing accumulation of predicted protein sequences by high-throughput genome sequencing for numerous and increasingly diverse organisms, the expansion of large-scale proteomics e. There is a widely recognized need for a centralized repository of protein sequences with comprehensive coverage and a systematic approach to protein annotation, incorporating, integrating and standardizing data from these various sources.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Advances in high-throughput and advanced technologies allow researchers to routinely perform whole genome and proteome analysis. For this purpose, they need high-quality resources providing comprehensive gene and protein sets for their organisms of interest. We will also illustrate how the complexity of the human proteome is captured and structured in UniProtKB. Database URL : www. The human proteome, as we define it in UniProt, is the set of protein sequences that can be derived by translation of all protein-coding genes of the human reference genome, including alternative products such as splice variants. Although curation of human proteins has always constituted the top priority in the UniProt Knowledgebase UniProtKB , the content of the human proteome in UniProtKB has evolved greatly in recent years, partly due to advances in technologies. The recent rise of big data and high-throughput technologies has shifted a number of paradigms in the scientific community. Although for decades, researchers focused on a single gene and its products, it is now common to work with whole genomes and proteomes.
Uniprotkb
All materials are free cultural works licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. Expert curation consists of a critical review of experimental and predicted data for each protein by a team of biologists, as well as manual verification of each protein sequence. UniProt curators extract biological information from the literature and perform numerous computational analyses. Data captured from the scientific literature includes information on protein and gene names, function, catalytic activity, cofactors, subcellular location, protein-protein interactions and much more.
Cook medical canton il
Open in new tab Download slide. More from Oxford Academic. The bibliography information is available via the website. Contents move to sidebar hide. My account. Proteome Res. Schaab C. To achieve accuracy, annotations are performed by biologists with specific expertise. New and updated sequences are loaded on a daily basis, cross-referenced to the source database accession number, and provided with a sequence version that increments upon changes to the underlying sequence. UniProtKB protein entries now have an enhanced view of publications relevant for a protein.
The aim of the UniProt Knowledgebase is to provide users with a comprehensive, high-quality and freely accessible set of protein sequences annotated with functional information.
Both UniRule and SAAS use the hierarchical InterPro classification of protein family and domain signatures 18 as a basis for protein classification and functional annotation. Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivs. For other proteins, there is experimental evidence such as Edman sequencing, clear identification by mass spectrometry MSI , X-ray or NMR structure, detection by antibodies, etc. Finally we provide the UniProt Archive UniParc that provides a complete set of known sequences, including historical obsolete sequences 3. Edde B. ISSN Receive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic. In addition, to complement this approach, we have developed a semi-automatic pipeline for integration of high-throughput proteomics data that is distinct from expert curation and which adds PTMs from manually evaluated large-scale proteomics publications In September , subcell. Schaab C. Forthcoming format change The protein names contained in the description DE lines of reviewed UniProtKB entries are widely used by scientists to unambiguously identify a protein and provide a definitive source nomenclature for the annotation of homologous proteins in new genomic sequences. Spastin specifically recognizes and cuts microtubules that are polyglutamylated: severing activity by spastin increases as the number of glutamates per tubulin rises from one to eight and decreases beyond this glutamylation threshold

0 thoughts on “Uniprotkb”