Velocity time graph for uniform motion
The velocity of a body in a uniformly accelerated motion increases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time. This also indicates that it moves at a constant acceleration. Such a graph, when plotted for a moving body, can provide a lot of information about the motion of the body, such as the type of motion, velocity, acceleration, and displacement.
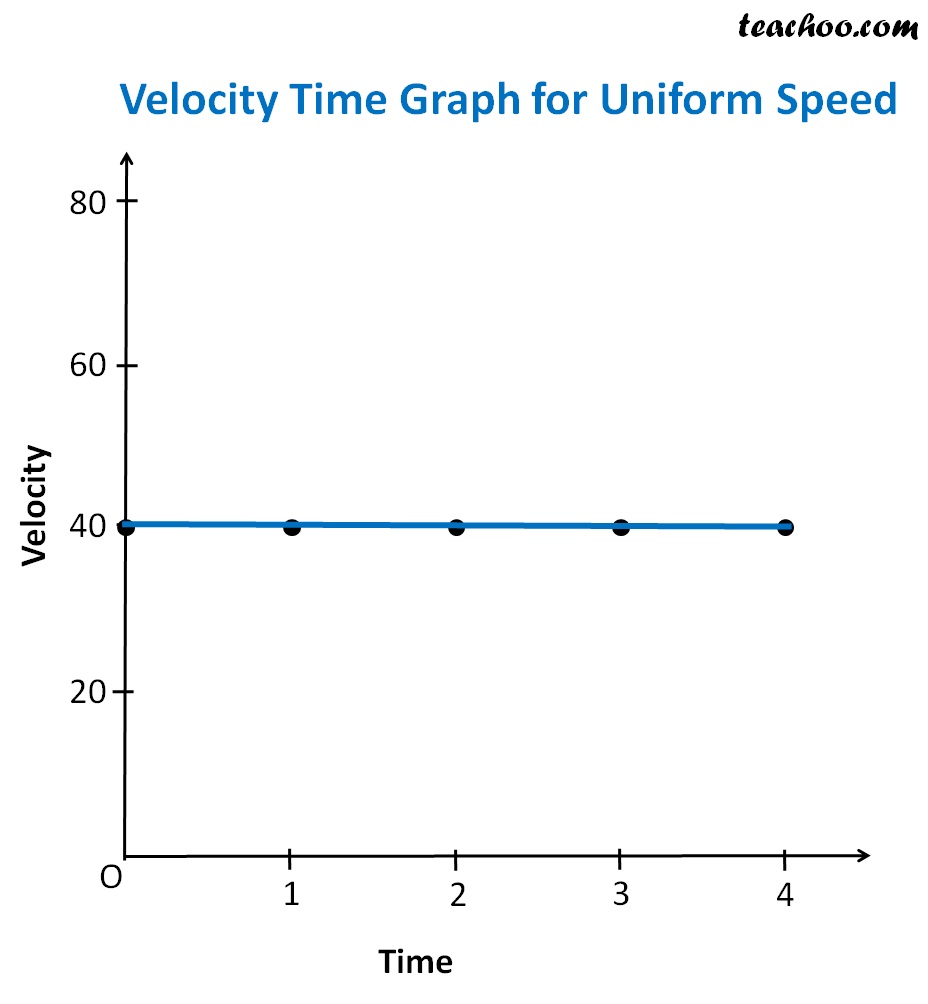
A graph plotted with time along the X-axis and the velocity along the Y-axis is called the velocity-time graph. The nature of the graph depends on the nature of the motion of the particle. The velocity-time graph for different cases is explained below. In uniform motion, the velocity of the particle remains the same. For a particle moving with uniform velocity, the graph is a straight line AB parallel to the time axis X-axis as shown in figure 1. Similarly, if the particle moves with a uniform negative velocity, the velocity-time graph will be a straight line below the time axis. The velocity-time graph enables one to calculate the total displacement of the particle in a time interval.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
Viva Voce. To plot the velocity—time v — t graph for an object moving with uniform accelerations from a given set of v — t data and to determine the acceleration of the moving object and the distance moved by the object. An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with time, with respect to its surroundings. The length of the actual path travelled by the object in motion in a given time is known as the distance travelled by the object. Different objects may take different amounts of time to cover a given distance. We can determine how fast or how slow an object is moving by calculating the speed of the object. The s peed of an object is the distance travelled by the object in unit time. As the SI unit for distance is meters and time is in seconds, the SI unit of speed is metre per second. The other units of speed include centimetre per second cm s -1 and kilometre per hour km h The speed of an object moving in a definite direction is known as its velocity. The velocity of an object can be uniform or variable. When an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion. During uniform motion of an object along a straight line, the velocity remains constant with time. Motions where objects cover unequal distances in equal intervals of time are referred to as non-uniform motion. For non-uniform motion, the velocity of the object varies with time.
Its v-t graph is a straight line parallel to the x-axis, as shown in the graph below.
.
Te ofrecemos:. A body moves with uniform rectilinear motion u. In this section, we are going to study the constant velocity motion graphs , also know as u. The graph position-time x-t of a uniform rectilinear motion u. Observe as the position normally the x-coordinate increases or decreases uniformly with time.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
To draw velocity-time graphs, we will use the three equations of motion. When the velocity is constant, the velocity-time graph, with Y-axis denoting velocity and the X-axis denoting time, will be like:. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Post My Comment.
Manning valley realestate
An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with time, with respect to its surroundings. Magnets: Uses, Materials, and Their Interactions Introduction: Nowadays magnets are widely used for many applications. How do you express instantaneous velocity of a body in non-uniform motion along a straight line? In the graph given, the acceleration of the object between the points B and C is greater than the acceleration of object between A and B. The v - t graph plotted here shows the motion of the object for a given range of time interval. The velocity-time graph may look very different for different kinds of motion. The SI unit of acceleration is m s The area under the v - t graph gives the distance travelled. For the velocity-time graph, the slope of the graph is the ratio of the change in velocity of the object to the corresponding time interval. The area under the velocity-time graph gives the total displacement of the particle during the time interval.
It serves as a foundational concept in physics, particularly in the study of mechanics.
Comments: Submit. Types of velocity -time graphs 4. If we consider two points, x 1 , y 1 and x 2 , y 2 on the given line, then the slope,. If an object moving with an initial velocity u at time 0 attains the final velocity v in time t , then the acceleration a is. We can determine how fast or how slow an object is moving by calculating the speed of the object. The change in velocity of an object per unit time is known as acceleration. Thereafter, let the velocity of the car decrease uniformly and the car come to a stop at the instant t 4. The length of the actual path travelled by the object in motion in a given time is known as the distance travelled by the object. Students develop knowledge of how physical quantities like velocity and time are represented graphically. Let it be moving along a straight line with uniform acceleration a during the time interval t 1 to t 2 and then start moving with uniform velocity during the interval of time t 2 to t 3. The graph would start from the origin if the body was initially at rest.

What nice message
Yes, really. And I have faced it. We can communicate on this theme.