What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy
Electron gain enthalpy is sometimes also referred to as Electron affinity although there is a minute difference between them. Electron gain enthalpy is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom. During the addition of an electron, energy can either be released or absorbed.
Electron gain enthalpy is nothing but the energy related to an affinity for the electron of an element. It is a tendency of an element towards electron addition to its outermost shell. The addition of electrons is not so easy as it is an energy-dependent process. The entire process is carried out with an element in its gaseous state. The size of the element has a great impact on the electron gain enthalpy as the nuclear attraction force on the valence shell varies with the size of an element. In this Chemistry article, you will get an idea about the Electron gain enthalpy in detail. Enthalpy is basically energy.
What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy
Electron gain enthalpy is simply another term used for electron affinity , which represents the change in enthalpy when one mole of electrons in added to one mole of atoms in the gaseous state. However , an important difference exists between the two terms. Electron gain enthalpy represents the heat given off by the ionization reaction, which means that it will carry a negative sign. On the other hand, electron affinity is viewed as the heat absorbed by the surroundings, and will thus carry a positive sign. Now, here's what you've got here. Since energy is being released by this reaction, i. At the same time, the fact that heat is being released by the reaction implies that heat is being absorbed by the surroundings. This means that chlorine's electron affinity will be positive. What is "electron-gain" enthalpy? I mean in relation to electron affinity.
But, what is electron gain enthalpy? Electron gain enthalpy is the tendency of an isolated gaseous atom to accept an additional electron to form a negative ion. View Result.
How many of you are aware of what electrons are? But, what is electron gain enthalpy? Well, not anymore! In this chapter, we will look at the concept of electron gain enthalpy and discuss it in greater detail. Electron gain enthalpy of an element is the energy released when a neutral isolated gaseous atom accepts an extra electron to form the gaseous negative Ion i.
Electron gain enthalpy is sometimes also referred to as Electron affinity although there is a minute difference between them. Electron gain enthalpy is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom. During the addition of an electron, energy can either be released or absorbed. Let us consider two metals Magnesium and Sodium. Metals lose electrons to obtain the inert gas configuration. Hence, Sodium and Magnesium atoms will not add electrons easily. Some external energy is needed to add the electron in their atoms.
What do you mean by electron gain enthalpy
How many of you are aware of what electrons are? But, what is electron gain enthalpy? Well, not anymore! In this chapter, we will look at the concept of electron gain enthalpy and discuss it in greater detail. Electron gain enthalpy of an element is the energy released when a neutral isolated gaseous atom accepts an extra electron to form the gaseous negative Ion i.
Suzyq menu
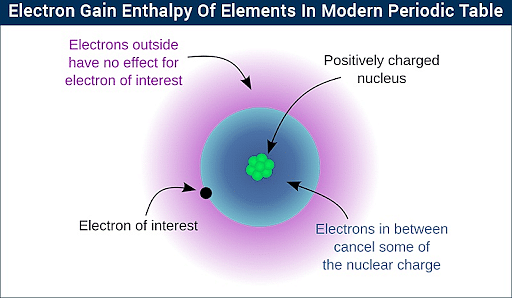
Thus, electron gain enthalpy results in more negative in a period when travelling from left to right. The electron gain enthalpy of halogens is the enthalpy change that occurs when an electron is added to a halogen atom in gaseous state. Dec 31, The sign of electron gain enthalpy and electron affinity is opposite for any element. At last we will discuss some important questions related to zwitterion. Why does electron gain enthalpy decrease down the group? Halogens have a highly negative electron gain enthalpy because they show a strong affinity to reach stable noble gas configuration. Related links. If the number of shielding electrons increases the effective nuclear charge decreases and negative electron gain enthalpy also decreases. Noble gases contain large positive electron gain enthalpy. After acquiring one electron it will achieve its noble gas configuration. To define electron gain enthalpy , sometimes, it is also called Electron affinity , although there exists a small difference between them. Ayushi September 14, at pm. The entire process may be energy releasing or energy absorbing that depends on the nature of the element.
The reaction can be given as below:.
Post My Comment. Related links. Download NEET question paper. Positive Electron Gain Enthalpy. The electron affinity decreases down the group because of increased atomic radius. Login To View Results. Related articles. So we can conclude that electron gain enthalpy depends on atomic radius and the nuclear charge. It was observed and concluded from experiments that in the first case of moving across the periodic table, the increase in nuclear charge defies the repulsion caused due to the additional electrons in the valence level or the outermost shell. Elements with exactly either half-filled or completely filled orbitals are very stable. This continuous increase of charge and force of attraction results in the electron gain enthalpy becoming more negative. Similar to it, we can also define the electron gain enthalpy of nitrogen.

It will be last drop.
It is a pity, that now I can not express - there is no free time. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
You commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.