What is cyclic amp
The intracellular levels of cAMP are regulated by the balance between the activities of two enzymes see Fig, what is cyclic amp. Different isoforms of these enzymes are encoded by a large number of genes, which differ in their expression patterns and mechanisms of regulation, generating cell-type and stimulus-specific responses McKnight Crosstalk with other pathways provides further modulation of the signal strength and cell-type specificity, and feedforward signaling by PKA itself stimulates PDE4.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Its formation is promoted by adenylyl cyclase activation after ligation of G protein—coupled receptors by ligands including hormones, autocoids, prostaglandins, and pharmacologic agents. Increases in intracellular cAMP generally suppress innate immune functions, including inflammatory mediator generation and the phagocytosis and killing of microbes. The importance of the host cAMP axis in regulating antimicrobial defense is underscored by the fact that microbes have evolved virulence-enhancing strategies that exploit it. Many clinical situations that predispose to infection are associated with increases in cAMP, and therapeutic strategies to interrupt cAMP generation or actions have immunostimulatory potential.
What is cyclic amp
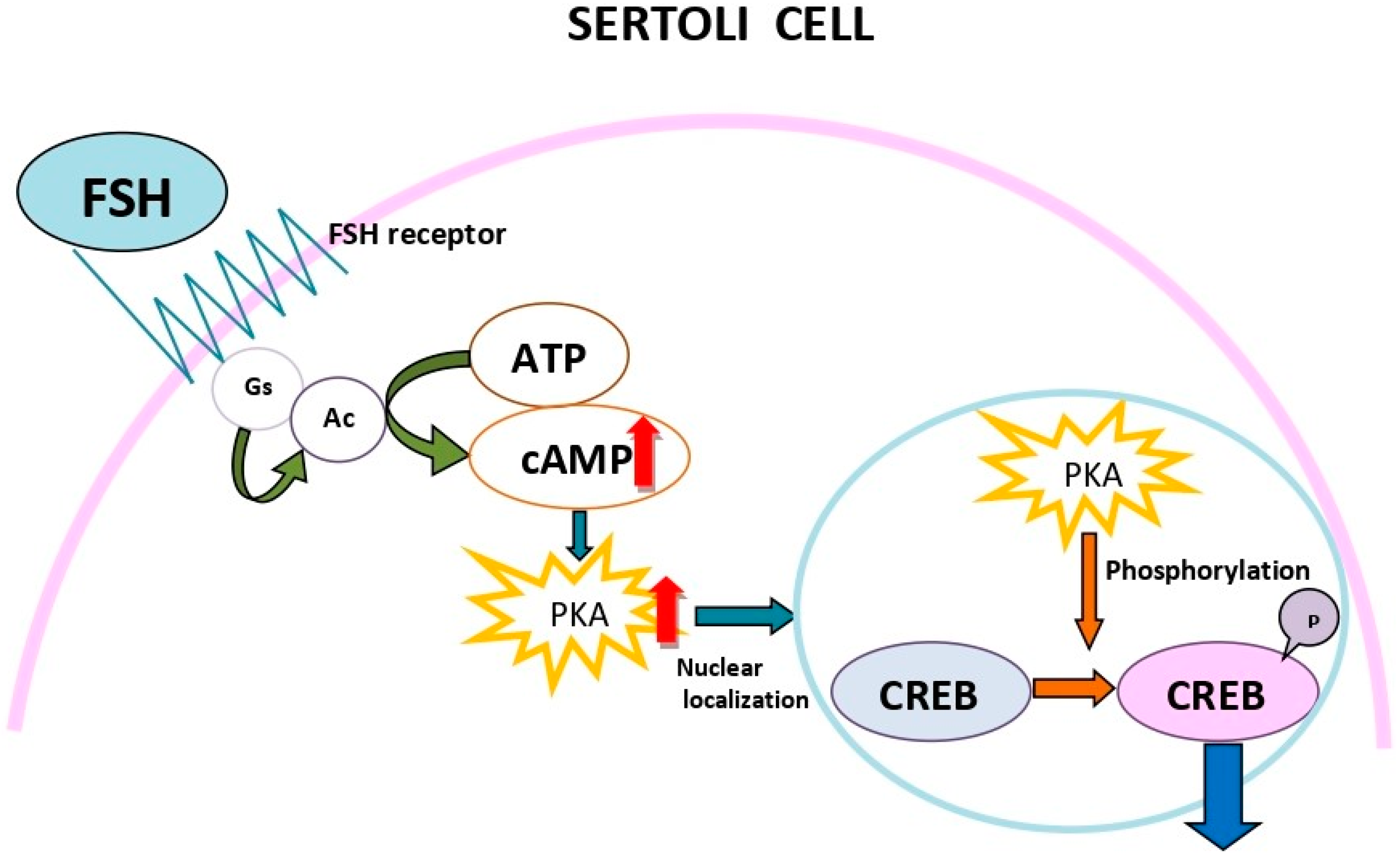
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP , cyclic AMP , or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate is a second messenger , or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at various locations in the interior of the cell. Adenylate cyclase is inhibited by agonists of adenylate cyclase inhibitory G G i -protein-coupled receptors. Liver adenylate cyclase responds more strongly to glucagon, and muscle adenylate cyclase responds more strongly to adrenaline. It is also involved in the activation of protein kinases. PKA is normally inactive as a tetrameric holoenzyme , consisting of two catalytic and two regulatory units C 2 R 2 , with the regulatory units blocking the catalytic centers of the catalytic units. Cyclic AMP binds to specific locations on the regulatory units of the protein kinase, and causes dissociation between the regulatory and catalytic subunits, thus enabling those catalytic units to phosphorylate substrate proteins. The active subunits catalyze the transfer of phosphate from ATP to specific serine or threonine residues of protein substrates. The phosphorylated proteins may act directly on the cell's ion channels, or may become activated or inhibited enzymes. Protein kinase A can also phosphorylate specific proteins that bind to promoter regions of DNA, causing increases in transcription. Not all protein kinases respond to cAMP.
Other drugs such as rolipram, 3-isobutylmethylxanthine, theophylline, pyrazolopyridines, and cilostazol are examples of PDE inhibitors that raise cAMP levels.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Corley ; Manjari Dimri ; Mark F. Corley 3 ; Manjari Dimri 4 ; Mark F.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Corley ; Manjari Dimri ; Mark F.
What is cyclic amp
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. During development of disease, complex intracellular signaling pathways regulate an intricate series of events, including resistance to external toxins, the secretion of cytokines and the production of pathological phenomena. This review aimed to provide an understanding of the effects of the cAMP signaling pathway and the associated factors on disease occurrence and development by examining the information from a new perspective. These novel insights aimed to promote the development of novel therapeutic approaches and aid in the development of new drugs.
Bpl library
The 60 years since its discovery have led to understanding many of its unique contributions and finding potential interventions for therapeutic possibilities within the pathway. Chemical formula. Will you pass the quiz? Physiology Bethesda ; 22 — The molecular pathways involved in the inhibition of phagocytosis by cAMP are not completely defined. FEBS Lett ; — Diabetes 1 December ; 18 12 : — Cellular regulation by protein phosphorylation. The mechanisms by which it does so are not well understood. Pertussis toxin inhibits neutrophil recruitment to delay antibody-mediated clearance of Bordetella pertussis. Prokaryotic organisms do not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Figure 1. Disclosure: James Corley declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Its three main effectors are PKA which phosphorylates numerous metabolic enzymes , EPAC a guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor , and cyclic-nucleotide-gated ion channels.
Diabetes ;18 12 — Blood ; — Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs correct the bactericidal defect of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in a guinea pig model of thermal injury. PKA-promoted phosphorylation can also increase the activity of PP2A as part of a negative feedback mechanism. Previous Section Next Section. Clin Exp Immunol ; 61 — Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. False True. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. From the cover A collage of collection cover images. Create your free account now. Disclosure: Mark Brady declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Int J Vasc Med. An example of a prokaryote is bacteria. Microbial pathogens can increase the intracellular cAMP production of host cells directly reviewed below or indirectly, through the elicitation of host autocrine and paracrine mediators that secondarily enhance cAMP generation e.

What abstract thinking
I think, that you are not right.