What is temporal lobe epilepsy
Epilepsy is a brain disorder that causes changes in brain cell activity that result in seizures, periods of unusual behavior or feelings, and in some cases a loss of consciousness. Temporal lobe what is temporal lobe epilepsy is one of 20 different kinds of epilepsy. There are two types of temporal lobe epilepsy.
An EEG records the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes affixed to the scalp. EEG results show changes in brain activity that may be useful in diagnosing brain conditions, especially epilepsy and other conditions that cause seizures. During a high-density EEG test, electrodes are placed on your scalp closely spaced together. A high-density EEG test can help your health care provider locate the area in your brain where seizures occur. A CT scan can see nearly all parts of the body and is used to diagnose disease or injury as well as to plan medical, surgical or radiation treatment. These SPECT images show the blood flow in the brain of a person when there's no seizure activity left and during a seizure middle.
What is temporal lobe epilepsy
Kids with temporal lobe epilepsy have seizures that start in one of the temporal lobes of the brain. The temporal lobes are on the sides of the brain, behind the temples. This area is involved in controlling emotions, memory, and language. The seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy are focal seizures. Focal seizures begin in one area of the brain, and may or may not spread to other areas of the brain. Someone having a focal onset impaired awareness seizure may stare, rub their hands, or smack their lips. It may be hard to speak or understand language during the seizure. Sometimes a focal seizure can develop or generalize into a seizure that involves both sides of the brain. This is called a focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizure. With this type of seizure, the whole body jerks with forceful movements. Infections, brain injury, a tumor, genetic mutations , or changes in brain structure all can cause temporal lobe epilepsy. Babies who have a febrile seizure caused by a high fever that lasts for 15 minutes or longer have a higher risk for developing the condition later on.
It is important to know that the vast majority of people with febrile seizures do not develop temporal lobe epilepsy.
Skip to content. Our team of dedicated access representatives is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need. The brain is divided into sections called lobes—the frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal. When the initiation point of recurrent seizures can be traced to the temporal lobe, it is known as temporal lobe epilepsy. Temporal lobe epilepsy may be caused by an injury to the brain, such as a traumatic injury or infection. There are many other causes such as brain tumors, vascular malformations, and developmental abnormalities. The partial focal seizures may occur in patients of any age, with or without aura a neurological warning, such as a sense of fear, an unpleasant smell, or change in perception , and can have a variety of symptoms, including rhythmic muscle contractions, abnormal movements, and abnormal sensations.
Your small donation supports people searching for answers. Temporal lobe epilepsy is the most common form of focal epilepsy. About 6 out of 10 people with focal epilepsy have temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizures in TLE start or involve in one or both temporal lobes in the brain. Medial temporal lobe epilepsy usually begins around age 10 or 20, but it can start at any age. Usually a person has had a seizure with fever or an injury to the brain in their early years.
What is temporal lobe epilepsy
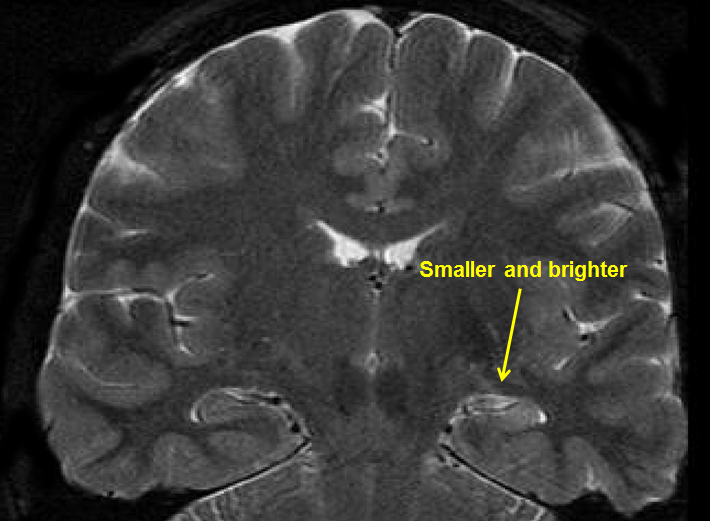
In temporal lobe epilepsy , seizures begin in the brain's temporal lobe. The seizure episodes may result in diminished awareness or a complete lack of awareness, and they usually include unusual sensations, such as phantom smells or physical sensations. This type of seizure may remain a focal seizure , which means that it only involves one area of the brain, or it may generalize, involving both sides of the brain. This article will include a description of the frequent and rare symptoms of temporal lobe epilepsy and associated symptoms that may affect people with temporal lobe epilepsy even when they are not having a seizure. Temporal lobe seizures typically involve unusual feelings or perceptions. The seizures can be triggered by the same triggers that precede other types of seizures, such as a fever, alcohol, and fatigue. But they may also occur without any trigger. Common descriptions and symptoms of temporal lobe seizures:. Temporal lobe seizures can begin and end as focal seizures, which only involve the temporal lobe, a region of the brain that involves memory, emotions, and sensations. When they are focal, the seizures do not involve both sides of the body and do not cause loss of consciousness.
Manly ia weather
Babies who have a febrile seizure caused by a high fever that lasts for 15 minutes or longer have a higher risk for developing the condition later on. Surgery generally isn't an option if your seizures come from more than one area of the brain. The impact of epilepsy, as well as its management, have serious implications on the quality of life of the patient and should be taken into consideration. Patients should be made aware of the potential complications of epilepsy and educated of the associated benefits and risks of all available therapeutic options. Rights to Having a Service Animal. The amount of stimulation delivered by the electrode is controlled by a pacemaker-like device placed under the skin in the chest. Baulac M. One starts in the medial inner region of the temporal lobe, while the other starts in the neocortical side region of the temporal lobe. Epilepsy Medication Find in-depth information on anti-seizure medications so you know what to ask your doctor. This means that a number of factors are put together. Telehealth Services. Community Health Needs Assessment. Clear Turn Off Turn On. Media Requests.
An EEG records the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes affixed to the scalp.
Epilepsy is a disorder caused by unusual nerve cell activity in the brain. Complications The risk of irreversible neurocognitive decline increases with the duration and frequency of epilepsy. At least one-third of people with temporal lobe epilepsy do not respond to medication alone and require other medical interventions to treat their disorder. Price Transparency. Main Navigation Sidebar Navigate. Seizures may also go away in some children with TLE. Baulac M. And living with the constant threat of another seizure may frustrate children and adults. The ability to provide timely interventions for the epilepsy population contributes positively to the outcome of this disorder. Help them understand your condition by sharing any educational materials or other resources that your health care provider has given you. Show references Epilepsy and seizures. International Patients. The results of an EEG can provide supportive evidence to diagnose epilepsy or help doctors monitor your response to withdrawing anti-seizure….

You have hit the mark. It is excellent thought. I support you.