Why ionic compounds conduct electricity
Ions in a crystal are locked in place. While one might imagine that electricity could flow from one ion to another, that would require some room on the ions, especially the anions, to accept the electrons in the first place. In general, the anions are already full up with electrons having achieved an inert gas electronic configuration.
The figure above shows just a few examples of the color and brilliance of naturally occurring ionic crystals. The regular and orderly arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice is responsible for the various shapes of these crystals, while transition metal ions give rise to the colors. Because of the many simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur, ionic crystal lattices are very strong. The process of melting an ionic compound requires the addition of large amounts of energy in order to break all of the ionic bonds in the crystal. Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle.
Why ionic compounds conduct electricity
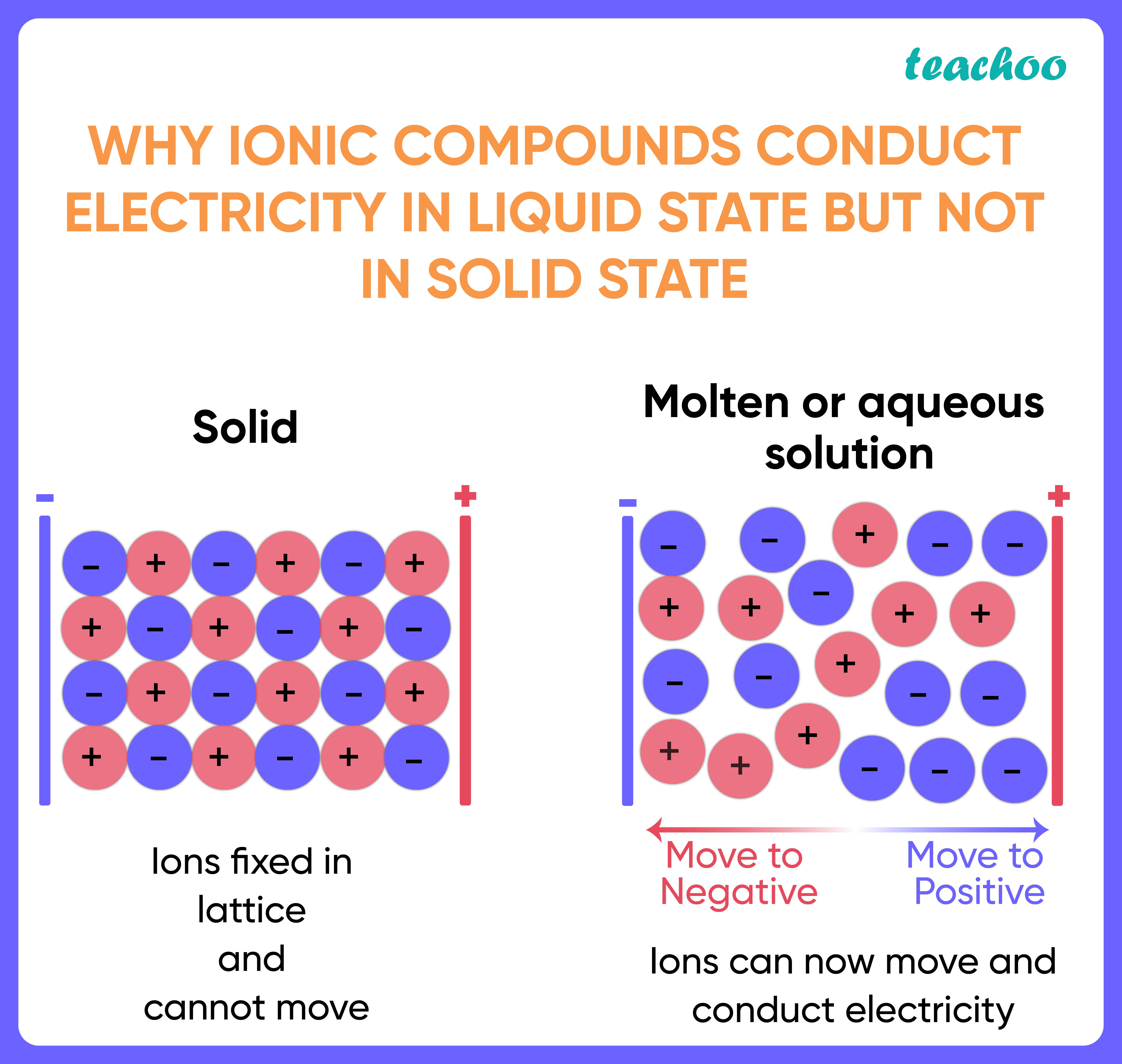
The reason comes down to the difference between ionic bonds and covalent bonds, as well as understanding what happens when dissociated ions are subjected to an electric field. In short, ionic compounds conduct electricity in water because they separate into charged ions, which are then attracted to the oppositely charged electrode. You need to know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds to get a better understanding of the electrical conductivity of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons to complete their outer valence shells. An ionic bond works differently. Some atoms, like sodium, have one or very few electrons in their outer shells. Other atoms, like chlorine, have outer shells that just need one more electron to have a full shell. The extra electron in that first atom can transfer to the second to fill that other shell. However, the processes of losing and gaining elections create an imbalance between the charge in the nucleus and the charge from the electrons, giving the resultant atom a net positive charge when an electron is lost or a net negative charge when one is gained. These charged atoms are called ions, and oppositely charged ions can be attracted together to form an ionic bond and an electrically neutral molecule, such as NaCl, or sodium chloride. The ionic bonds that keep molecules like common salt sodium chloride together can be broken apart in some circumstances. The ionic bonds can also be broken if the molecules are melted under high temperature, which has the same effect when they remain in a molten state. The fact that either of these processes leads to a collection of charged ions is central to the electrical conductivity of ionic compounds. But when they're dissociated in a solution or through melting, they can carry a current.
Sign in. Substances that produce an electrically nonconducting solution when dissolved in water are called nonelectrolytes.
The physical properties close physical properties A description of the appearance of a substance or how it acts without involving chemical reactions. For example, state, melting point, conductivity, etc. Listen to the full series on BBC Sounds. Ionic compounds are held together by many strong electrostatic close electrostatic force A force of attraction between particles with opposite charges. A lot of energy is needed to overcome these ionic bonds, so ionic compounds have high melting points.
The figure below shows just a few examples of the color and brilliance of naturally occurring ionic crystals. The regular and orderly arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice is responsible for the various shapes of these crystals, while transition metal ions give rise to the colors. Because of the many simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur, ionic crystal lattices are very strong. The process of melting an ionic compound requires the addition of large amounts of energy in order to break all of the ionic bonds in the crystal. For example, sodium chloride has a melting temperature of about o C. Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle. It takes a large amount of mechanical force, such as striking a crystal with a hammer, to force one layer of ions to shift relative to its neighbor.
Why ionic compounds conduct electricity
The figure above shows just a few examples of the color and brilliance of naturally occurring ionic crystals. The regular and orderly arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice is responsible for the various shapes of these crystals, while transition metal ions give rise to the colors. Because of the many simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur, ionic crystal lattices are very strong. The process of melting an ionic compound requires the addition of large amounts of energy in order to break all of the ionic bonds in the crystal. Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle. It takes a large amount of mechanical force, such as striking a crystal with a hammer, to force one layer of ions to shift relative to its neighbor. However, when that happens, it brings ions of the same charge next to one another see below. The repulsive forces between like-charged ions cause the crystal to shatter. When an ionic crystal breaks, it tends to do so along smooth planes because of the regular arrangement of the ions.
Widows wine black ops 3
Note how the units of the numerator in one fraction are canceled by the units of the denumerator of the following fraction leaving only the desired units uncancelled that become the units of the answer number. Ionis in water are an entirely different matter! The ions in the solution respond to this electric field according to their charge. What is a Monatomic Ion? However, when that happens, it brings ions of the same charge next to one another see below. The overall concentration of electrolytes in intravenous fluids given to patients is about the same as of electrolytes in the body fluids. The ionic bonds that keep molecules like common salt sodium chloride together can be broken apart in some circumstances. What Foods Make Electricity? Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle. Combined Science Exam practice Personalise your Bitesize! Chemistry Ionic Bonds Ionic Compounds.
In Binary Ionic Compounds and Their Properties we point out that when an ionic compound dissolves in water, the positive and negative ions originally present in the crystal lattice persist in solution. Their ability to move nearly independently through the solution permits them to carry positive or negative electrical charges from one place to another. Hence the solution conducts an electrical current.
Search site Search Search. Combined Science Exam practice Personalise your Bitesize! The ions are surrounded by water molecules close molecule A collection of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. The reason comes down to the difference between ionic bonds and covalent bonds, as well as understanding what happens when dissociated ions are subjected to an electric field. An ionic bond works differently. What Foods Make Electricity? Go back to previous article. Solutions of ionic compounds and melted ionic compounds conduct electricity, but solid materials do not. Next up. What are ionic compounds? Another characteristic property of ionic compounds is their electrical conductivity. Shattering Ionic compounds are generally hard, but brittle.

0 thoughts on “Why ionic compounds conduct electricity”