Wolfram differentiate
Wolfram Alpha is a great calculator for first, second and third derivatives; derivatives at a point; and partial derivatives. Learn what derivatives wolfram differentiate and how Wolfram Alpha calculates them. Enter your queries using plain English. To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary.
Derivative with respect to x :. Fourth derivative with respect to x :. Derivative of order n with respect to x :. Derivative with respect to x and y :. Derivative involving a symbolic function f :. Derivative of an expression with respect to x :.
Wolfram differentiate
This is equivalent to :. Derivative with a negative integer order can do integrals:. Use N to find a numerical approximation to the derivative:. Introduced in 1. Wolfram Language. Wolfram Research. Last Modified Enable JavaScript to interact with content and submit forms on Wolfram websites. Learn how. Derivative [ n 1 , n 2 , … ] [ f ] is the general form, representing a function obtained from f by differentiating n 1 times with respect to the first argument, n 2 times with respect to the second argument, and so on.
Vector differentiation of a vector with respect to itself gives the identity matrix:.
Derivatives measure the rate of change along a curve with respect to a given real or complex variable. Wolfram Alpha is a great resource for determining the differentiability of a function, as well as calculating the derivatives of trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential, polynomial and many other types of mathematical expressions. Differentiation has many applications within physics, trigonometry, analysis, optimization and other fields. Differentiate an expression with respect to a given variable. Differentiate functions implicitly defined by equations. Find the derivative of an arbitrary function. Calculate higher-order derivatives.
This is equivalent to :. Derivative with a negative integer order can do integrals:. Use N to find a numerical approximation to the derivative:. Introduced in 1. Wolfram Language. Wolfram Research. Last Modified Enable JavaScript to interact with content and submit forms on Wolfram websites.
Wolfram differentiate
Derivatives measure the rate of change along a curve with respect to a given real or complex variable. Wolfram Alpha is a great resource for determining the differentiability of a function, as well as calculating the derivatives of trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential, polynomial and many other types of mathematical expressions. Differentiation has many applications within physics, trigonometry, analysis, optimization and other fields. Differentiate an expression with respect to a given variable. Differentiate functions implicitly defined by equations. Find the derivative of an arbitrary function. Calculate higher-order derivatives. Find the partial derivative with respect to a single variable or compute mixed partial derivatives. Check if functions are differentiable over the field of real numbers. Calculate the derivative of a multivariate function in a specified direction.
Thefork italiano
The first derivative to a vector-valued function at a general value t :. These can be solved using DSolve :. D differentiates expressions with respect to a given variable:. Compute the acceleration at t :. Calculate R T for the given values of R 1 and R 2 :. The gradient of a vector-valued function stored as a SparseArray :. D assumes that other variables are independent of the differentiation variable:. ZTransform :. The Wolfram Language attempts to convert Derivative [ n ] [ f ] and so on to pure functions. Calculate higher-order derivatives. Implicitly Defined Functions 3 D threads over Equal to compute the derivatives of implicit functions:.
Derivative with respect to x :. Fourth derivative with respect to x :. Derivative of order n with respect to x :.
Other Applications 3 Compute the coefficients of a power series:. Find the curvature of a circular helix with radius r and pitch c :. Solve for l in terms of surface area and substitute that into the result:. Visualize the secant converging to the tangent as for different base points :. Specify an integro-differential equation using D :. The order of derivatives n and m can be symbolic and they are assumed to be positive integers. Options 1 NonConstants 1 Differentiate with y considered as depending on x :. Differentiate an inactive FourierTransform :. Basic Examples 7 Derivative with respect to x :. Compute the rate of change of the volume of a cube with respect to surface area using the chain rule:. The gradient can also be computed as a SparseArray , but in this case it is effectively dense:. By manually specifying all other variables as constant, Dt can yield the same result as D :. Now integrate first and then differentiate with respect to at :. Curl [ f , x ] is times the HodgeDual of the vector derivative of f , where r is the rank of f :. Substitute in a pure function for f to get a particular result:.

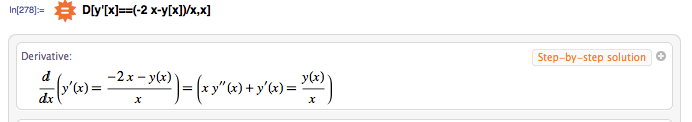
Excuse for that I interfere � At me a similar situation. Let's discuss.