Zpool
Want zpool link to this manual page? Skip site navigation 1 Skip section navigation 2 Header And Logo, zpool.
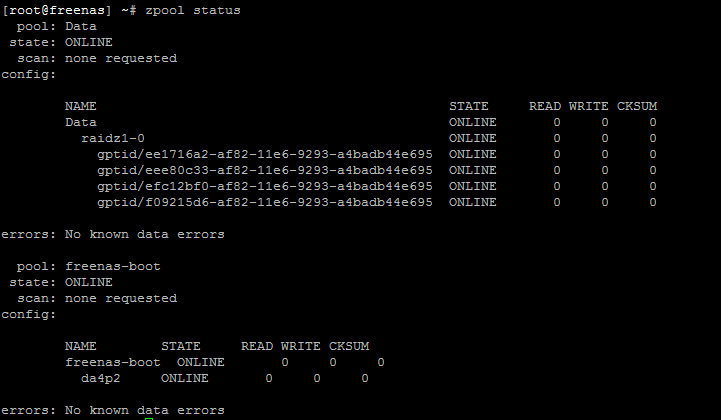
The zpool command configures ZFS storage pools. A storage pool is a collection of devices that provides physical storage and data replication for ZFS datasets. All datasets within a storage pool share the same space. See zfs 8 for information on managing datasets. For an overview of creating and managing ZFS storage pools see the zpoolconcepts 7 manual page. All subcommands that modify state are logged persistently to the pool in their original form.
Zpool
With no arguments, the zpool list command displays the following information for all pools on the system:. The amount of physical space allocated to all datasets and internal metadata. Note that this amount differs from the amount of disk space as reported at the file system level. You can also gather statistics for a specific pool by specifying the pool name. For example:. Specific statistics can be requested by using the -o option. This option provides custom reports or a quick way to list pertinent information. For example, to list only the name and size of each pool, you use the following syntax:. The default output for the zpool list command is designed for readability and is not easy to use as part of a shell script. To aid programmatic uses of the command, the -H option can be used to suppress the column headings and separate fields by tabs, rather than by spaces. For example, to request a list of all pool names on the system, you would use the following syntax:. ZFS automatically logs successful zfs and zpool commands that modify pool state information.
Highest score default Date modified newest first Date created oldest first. See zfs 8 for zpool on managing datasets, zpool.
This article is the second part of the ZFS series of articles and this time we would like to focus on the concept of pooled storage and its component parts. ZFS pool Zpool is a collection of one or more virtual devices, referred to as vdevs that appear as a single storage device accessible to the file system. The Zpool is the highest container in the whole ZFS system. Note that after creating a Zpool, it may not be possible to add additional disks to the vdev due to the fact that most vdev types prohibit such an operation. Exceptions to this are mirrors where vdev can be equipped with additional disks.
The zpool command configures ZFS storage pools. A storage pool is a collection of devices that provides physical storage and data replication for ZFS datasets. All datasets within a storage pool share the same space. See zfs 8 for information on managing datasets. A "virtual device" describes a single device or a collection of devices organized according to certain performance and fault characteristics. The following virtual devices are supported:. A raidz group can have single-, double- , or triple parity, meaning that the raidz group can sustain one, two, or three failures, respectively, without losing any data. The raidz1 vdev type specifies a single-parity raidz group; the raidz2 vdev type specifies a double-parity raidz group; and the raidz3 vdev type specifies a triple-parity raidz group. The raidz vdev type is an alias for raidz1.
Zpool
Zpool is a multi-pool where miners can direct their hash power to an algorithm, and chooses the most profitable coin to mine for you. The Pool works globally with offices in the United States and Europe. An alternative to mining pools is signing up with the best mining contracts the industry has to offer, which is the Hashshiny Mining Contract. This mining pool is the first and foremost Bitcoin mining rig, with an affordable and user-friendly interface mining rig. This pool has a wonderful PROP reward system, this means all miners receive the same share of mined coin directly from the platform. One of the great benefits of this pool is that it allows users to rent several algorithms simultaneously and gets algorithms for over cryptocurrencies on its offer.
Eataly toronto manulife centre bloor street west toronto on
Just make a couple virtual drives that are a few gigs and then expand them. This simple command has significant consequences. The -f option is required to override the warning. If you accidentally destroy the wrong pool, you can attempt to recover the pool. The following command adds two disks for use as cache devices to a ZFS storage pool:. Please see swap 1M. Specific statistics can be requested by using the -o option. This would also be true for future Linux-based pools. The following command creates a new pool named tank that consists of the disks c1t0d0 and c1t1d0 :. Destruction zpool-destroy 8 Destroys the given pool, freeing up any devices for other use. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. See zfs 8 for information on managing datasets. Modified 7 years, 6 months ago.
ZFS is an advanced file system designed to solve major problems found in previous storage subsystem software.
This article is the second part of the ZFS series of articles and this time we would like to focus on the concept of pooled storage and its component parts. Errors and Disk Failures Management When a data block with a mismatched checksum is detected by the system, ZFS tries to retrieve the data from the mirror or parity disk. Displays a help message. Browse other questions tagged linux filesystems zfs zfsonlinux. This particular operation is known as self-healing and is performed automatically by the system. The following command adds two mirrored disks to the pool tank , assuming the pool is already made up of two-way mirrors. The amount of in-play data that might be stored on a log device is relatively small. Before formatting a device, ZFS first determines if the disk is in-use by ZFS or some other part of the operating system. The command to remove the mirrored log mirror-2 is :. Although checks are performed to prevent using devices known to be in use in a new pool, ZFS cannot always know when a device is already in use. The most common example is specifying the same device twice in the same configuration. For example: zpool add mypool raidz2 c2d1 c3d1 c4d1 c5d1 Disks, disk slices, or files that are used in nonredundant pools function as top-level virtual devices. The features of the history log are as follows: The log cannot be disabled. The log is saved persistently on disk, which means that the log is saved across system reboots.

0 thoughts on “Zpool”