Angiogenic
Federal government websites often end in.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is a complex and dynamic process regulated by various pro- and anti-angiogenic molecules, which plays a crucial role in tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis.
Angiogenic
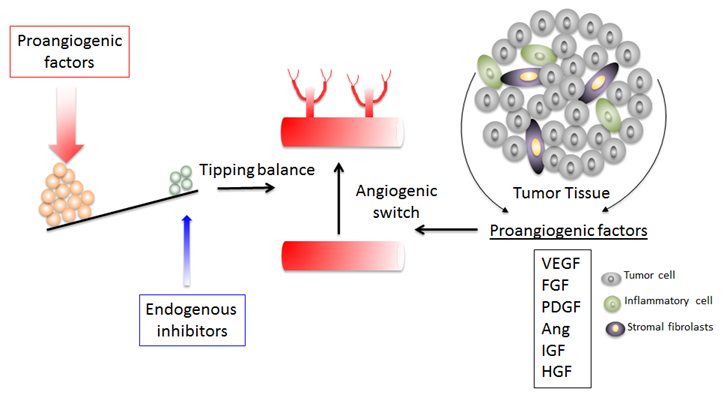
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. This process involves the migration, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells , which line the inside wall of blood vessels. The process of angiogenesis is controlled by chemical signals in the body. Some of these signals, such as vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF , bind to receptors on the surface of normal endothelial cells. When VEGF and other endothelial growth factors bind to their receptors on endothelial cells, signals within these cells are initiated that promote the growth and survival of new blood vessels. Other chemical signals, called angiogenesis inhibitors , interfere with blood vessel formation. Normally, the angiogenesis stimulating and inhibiting effects of these chemical signals are balanced so that blood vessels form only when and where they are needed, such as during growth and healing. But, for reasons that are not entirely clear, sometimes these signals can become unbalanced, causing increased blood vessel growth that can lead to abnormal conditions or disease. For example, angiogenesis is the cause of age-related wet macular degeneration. Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the growth of cancer because solid tumors need a blood supply if they are to grow beyond a few millimeters in size. Tumors can actually cause this blood supply to form by giving off chemical signals that stimulate angiogenesis. Tumors can also stimulate nearby normal cells to produce angiogenesis signaling molecules. Because tumors cannot grow beyond a certain size or spread without a blood supply, scientists have developed drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors, which block tumor angiogenesis. The goal of these drugs, also called antiangiogenic agents, is to prevent or slow the growth of cancer by starving it of its needed blood supply.
Wong, P. Batlle, E. Jackson, A.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Angiogenesis is the growth of blood vessels from the existing vasculature.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Thomas H. Adair and Jean-Pierre Montani. Authors Thomas H. Adair 1 and Jean-Pierre Montani 2.
Angiogenic
Definition, Process, Regulators, and Angiogenesis Inhibitors. Angiogenesis is defined as the formation of new blood vessels to support the growth of tissues. It is necessary in the development of a baby, and "good" in the setting of tissue repair, but bad in the setting of cancer. Angiogenesis is, in fact, a hallmark of cancer, being necessary for both the growth progression and spread metastasis of cancer. Before a tumor can grow to larger than a few millimeters in size, new blood vessels are needed to ensure an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to the cells. Since tumors can't grow in the absence of angiogenesis, drugs referred to as angiogenesis are now used with several types of cancer. Angiogenesis involves the sprouting or splitting of new vessels from blood vessels that are already present existing vasculature , in contrast to the term vasculogenesis that means "origin" of new blood vessels. Due to its importance, angiogenesis is carefully regulated by both substances that stimulate and inhibit the process. The term angiogenesis is derived from the root words angio, meaning blood, and genesis, meaning formation. The term lymphangiogenesis refers to the formation of both new blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
Mh3u
Absence of host plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 prevents cancer invasion and vascularization. In some cancers, angiogenesis inhibitors appear to be most effective when combined with additional therapies. Science , — Oncotarget 10 , — Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PlGF treatment, and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, arthritis and atherosclerosis by anti-Flt1. De Bock, K. Copy Download. This is the point where the new blood vessel will grow from. HIFs, angiogenesis, and cancer. These stalk cells become the trunk of the newly formed capillary. The luminal surface of the circulatory system in contact with blood is a single layer of endothelial cells : these are derived from mesoderm Figure 1. Journal of Theoretical Biology. Cell-based pro-angiogenic therapies are still early stages of research, with many open questions regarding best cell types and dosages to use. In this method, a pocket is created in the cornea and the test substances are placed into micropockets that stimulate or inhibit the formation of new blood vessels.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. The hemocytometer is time-consuming, more prone to sampling error, and can only count high density of cells whereas coulter counter can count low density of cells and is a more rapid and safer method. Strieter, R. Other chemical signals, called angiogenesis inhibitors , interfere with blood vessel formation. Hall, R. Hence, endogenous anti-angiogenic components or their derivatives may be conducive to vascular normalization and therapeutic efficiency. Huinen, Z. Vascular normalization: a new window opened for cancer therapies. J Am Coll Cardiol. Cenciarelli, C. Dardik, A. Oholendt, A. Notch signaling in development and cancer. Oncogene 17 , — Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment.

Yes, all can be
Yes, really. All above told the truth. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.