Climate of japan wikipedia
Japan [a] is an island country in East Asia. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fireand spans an archipelago of 14, islandswith the five main islands being HokkaidoHonshu the "mainland"climate of japan wikipedia, ShikokuKyushuand Okinawa.
Three years ago, you began to feel restless. Not "time to take up a new hobby" restless, but more like "time to travel the world and have exciting, new experiences" restless. So you came up with a plan. An incredible, ridiculous plan. You decided to move to Japan… and live in the wilderness 1.
Climate of japan wikipedia
The Japan heatwave was a heatwave that affected many prefectures. Temperatures peaked at In June , high pressure over the Pacific Ocean caused a south to south-westerly flow of air, introducing hotter air from the tropics to Japan, fuelling higher temperatures. Japan's rainy season was declared over on 27 June, 22 days earlier in the year than usual, and the earliest end since Tokyo suffered an extreme heatwave one hundred years earlier, which peaked at Japan was also badly affected by the Northeast Asia heat wave , which saw Overall, the summer of was the second hottest on record for Japan. Nuclear power stations were used to meet the increased demand for electricity. Insurance companies Sompo Holdings and Sumitomo Life Insurance both started offering insurance policies designed to cover costs associated with heatstroke. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk.
Toggle limited content width. Fukuoka The World Bank.
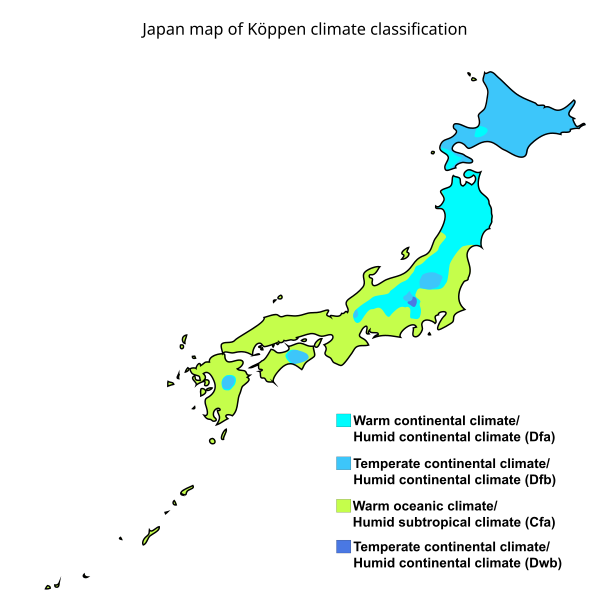
Japan is generally a rainy country with high humidity. As Mount Fuji and the Japanese coastal Alps provide a rain shadow, Nagano and Yamanashi Prefectures receive the least precipitation in Honshu, though it still exceeds millimetres 35 in annually. A similar effect is found in Hokkaido, where Okhotsk Subprefecture receives as little as millimetres 30 in per year. All other prefectures have coasts on the Pacific Ocean, Sea of Japan, and Seto Inland Sea, or have a body of salt water connected to them. Two prefectures— Hokkaido and Okinawa —are composed entirely of islands. The climate from June to September is marked by hot, wet weather brought by tropical airflows from the Pacific Ocean and Southeast Asia. Maximum precipitation, like the rest of East Asia, occurs in the summer months except on the Sea of Japan coast where strong northerly winds produce a maximum in late autumn and early winter.
Japan Glances. Stretching like a bow off the east of the Eurasian continent, the Japanese archipelago shows great climatic variation within its approximately 3, kilometers of length from northeast to southwest. In winter, winds from Siberia pick up moisture as they cross the water, bringing rain and snow to the Japan Sea side of the country. Buffered by the central mountain ranges, the Pacific side of Japan enjoys fine weather in winter. By contrast, in summer the Pacific side of the country is rainier, due in part to typhoons, while the Japan Sea side has mostly sunny days. List created by Nippon. The first strong south wind of the year heralds the coming of spring to people on the Pacific side of Japan. Cherry blossom season with its hanami picnics under the trees starts in Okinawa in January. As well as the standard four seasons, most of Japan has a rainy season known as tsuyu , lasting around six weeks from late spring or early summer, depending on the area. In these sudden localized downpours, more than 50 millimeters of rain falls per hour.
Climate of japan wikipedia
Japan is an archipelagic country comprising a stratovolcanic archipelago over 3, km 1, mi along the Pacific coast of East Asia. The other 14, islands are classified as "remote islands" by the Japanese government. The territory covers , The subduction plates have pulled the Japanese archipelago eastward, created the Sea of Japan , and separated it from the Asian continent by back-arc spreading 15 million years ago. The climate varies from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical and tropical rainforests in the south.
Roleplay map codes
Retrieved December 1, Irrigation demand could be increased by higher temperatures due to higher plant evapotranspiration. This section needs expansion. Retrieved September 26, In the period of rapid economic growth after World War II, environmental policies were downplayed by the government and industrial corporations; as a result, environmental pollution was widespread in the s and s. Yes, add me to your mailing list. Deep reads from The Japan Times. An incredible, ridiculous plan. The Atlantic. Main article: Religion in Japan. Precipitation is very heavy, especially during the rainy season. Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians.
Japan has four distinct seasons with a climate ranging from subarctic in the north to subtropical in the south. Conditions are different between the Pacific side and the Sea of Japan side.
There are currently 64 grids from all over the world available in the package and you specify them using the grid argument. The Wall Street Journal. Komatsu, Ishikawa 31 Jul In , torrential rains caused flash floods and landslides, resulting in more than deaths the evacuation of 2. Download as PDF Printable version. Compared to the more northerly parts of the country, the subtropical region features a longer spring and autumn, and thus a more even balance between the four seasons. International Security. About Filters. In Japan, under a low emissions scenario, the total labor force is estimated to decrease by 0. Retrieved August 4,

0 thoughts on “Climate of japan wikipedia”