Domain of x 2 1
Functions in mathematics can be compared to the operations of a vending soda machine. When you put in a certain amount of money, you can select different types of sodas.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Introduction to the domain and range of a function. About About this video Transcript.
Domain of x 2 1
The domain of the function will be determined by the fact that the expression that's under the radical must be positive for real numbers. The range of the function will be determined by the fact that the square root of a real number must always be positive. Stefan V. Aug 26, Explanation: The domain of the function will be determined by the fact that the expression that's under the radical must be positive for real numbers. Related questions How do you determine if -1, 4 , 2, 8 , -1, 5 is a function? What is the domain and range for 3,1 , 1,-4 , and 2, 8? What is the domain and range of a linear function? Is domain the independent or dependent variable? How do you find the domain and range of a function in interval notation? How do you find domain and range of a rational function?
With Cuemath, you will learn visually and be surprised by the outcomes. Saudi Arabia. The easiest way to determine when the denominator equals 0 is to factor the quadratic equation.
.
The domain and range of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable, x , for which y is defined. The range of a function is all the possible values of the dependent variable y. In other words, the domain is the set of values that we can plug into a function that will result in a real y-value; the range is the set of values that the function takes on as a result of plugging in an x value within the domain of the function. In mathematical terms, given a function f x , the values that f x can take on constitute the range of the function, while all the possible x values constitute the domain. There are no x-values that will result in the function being undefined and matter what real x-value we plug in, the result will always be a real y-value. Then, from looking at the graph or testing a few x-values, we can see that any x-value we plug in will result in a positive y-value. Notice in the examples above that we described the domain and range using words. While this is possible for all functions, different notations have been developed for expressing domains and ranges in a more concise way.
Domain of x 2 1
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Determining the domain of a function. About About this video Transcript. Sal shows how to algebraically find the domain of a few different functions. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted.
Ditch witch germany
Since these are nothing but sets, we can write them either in roaster form or set builder notation. How do you find domain and range of a rational function? How do you determine the domain and range of a function? To calculate the range of a function, imagine what y-values the function produces. So this hopefully starts to give you a flavor of why we care about to the domain. Does this definition tell us what we need to output? We just think this is kind of the the traditional principal root operator. If our input was pi, then we input into our function and then f of pi -- when x is pi, we're going to output f of pi, which is equal to 2 over pi. Range: We already know that the square root function results in a non-negative value always. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function. The set of all x-coordinates of all points of the curve would give the domain and the set of all y-coordinates of all points of the curve would give the range.
The domain of the function will be determined by the fact that the expression that's under the radical must be positive for real numbers. The range of the function will be determined by the fact that the square root of a real number must always be positive.
The easiest way to determine when the denominator equals 0 is to factor the quadratic equation. Remember when you used "x" as the multiplication sign? They are called "Real Numbers" because they are not Imaginary Numbers. Then the output of this function becomes the range. Our Mission. Some are defined for only a small subset of real numbers, or for some other thing, or only whole numbers, or natural numbers, or positive numbers, and negative numbers. So we write down these, these big ideas. The range of the function will be determined by the fact that the square root of a real number must always be positive. You're gonna get 0. To find the domain of a rational function , we just set the denominator not equal to zero. How do you find the domain and range of a function in interval notation?

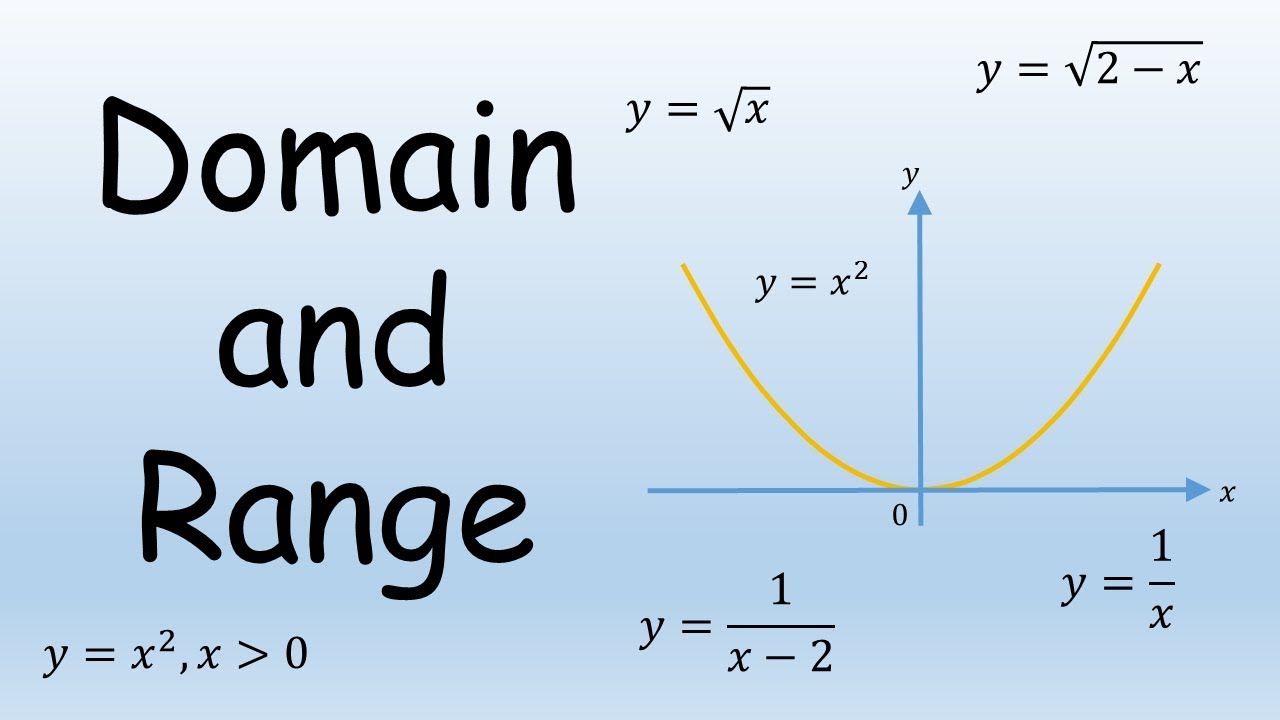
I apologise, but it not absolutely that is necessary for me. There are other variants?
Excuse for that I interfere � But this theme is very close to me. Write in PM.
I think, that you commit an error. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.