Goblet cell diagram
Goblet cell. They are found inside the trachea, bronchi, small and large intestine, goblet cell diagram, and conjunctiva in the eyes. Structure cell nucleus and other organelles. A type of ciliated columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract as respiratory mucosa including goblet cell, basal and ciliated cells, mucus.
Figure 1. Self drawn diagram of ciliated columnar epithelium. Ciliated columnar epithelial cells are found mainly in the tracheal and bronchial regions of the pulmonary system and also in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system. Ciliated columnar epithelium in the pulmonary system is interspersed with goblet cells that secrete mucous to form a mucosal layer apical to the epithelial layer see Figure 2. The rowing-like action of epithelial cilia work in tandem with goblet cells to propel mucus away from the lungs, preventing particulate matter from causing infection see Video 1. Video 1.
Goblet cell diagram
Most epithelial tissues are essentially large sheets of cells covering all the surfaces of the body exposed to the outside world and lining the outside of organs. Epithelium also forms much of the glandular tissue of the body. Skin is not the only area of the body exposed to the outside. Other areas include the airways, the digestive tract, as well as the urinary and reproductive systems, all of which are lined by an epithelium. Epithelial cells derive from all three major embryonic layers. The epithelia lining the skin, parts of the mouth and nose, and the anus develop from the ectoderm. Cells lining the airways and most of the digestive system originate in the endoderm. The epithelium that lines vessels in the lymphatic and cardiovascular system derives from the mesoderm and is called an endothelium. All epithelia share some important structural and functional features. This tissue is highly cellular, with little or no extracellular material present between cells. Adjoining cells form a specialized intercellular connection between their cell membranes called a cell junction. The epithelial cells exhibit polarity with differences in structure and function between the exposed or apical facing surface of the cell and the basal surface close to the underlying body structures. The basal lamina , a mixture of glycoproteins and collagen, provides an attachment site for the epithelium, separating it from underlying connective tissue. The basal lamina attaches to a reticular lamina , which is secreted by the underlying connective tissue, forming a basement membrane that helps hold it all together. Epithelial tissues are nearly completely avascular.
Portals : Biology Medicine. Anatomical terms of microanatomy [ edit on Wikidata ].
There are four types of basic tissues in the body: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous tissue. Goblet cells are found in epithelial tissue of Gastrointestinal tract and Respiratory tract. Following is a microscopic view and a diagram of epithelial tissue of the respiratory tract showing goblet cells. This is a diagram of a goblet cell:. In what kind of tissue can goblet cells can be found?
Goblet cells are specialized epithelial cells found in various mucosal surfaces throughout the body. This article explores the histology of goblet cells, revealing their microscopic structure, cellular components, and the vital role they play in producing and secreting mucus to protect and lubricate epithelial tissues. The primary function of goblet cells is the production and secretion of mucus. Mucus serves several important roles in maintaining the health and functionality of epithelial tissues:. The production and secretion of mucus by goblet cells are regulated by various factors, including immune signals, neuronal input, and environmental stimuli. Dysregulation of goblet cell function can contribute to certain disorders:. The histology of goblet cells reveals their microscopic structure and their crucial role in producing and secreting mucus to protect and lubricate epithelial tissues. By forming a protective barrier, trapping pathogens, and facilitating proper epithelial cell function, goblet cells contribute to the overall health and function of mucosal surfaces.
Goblet cell diagram
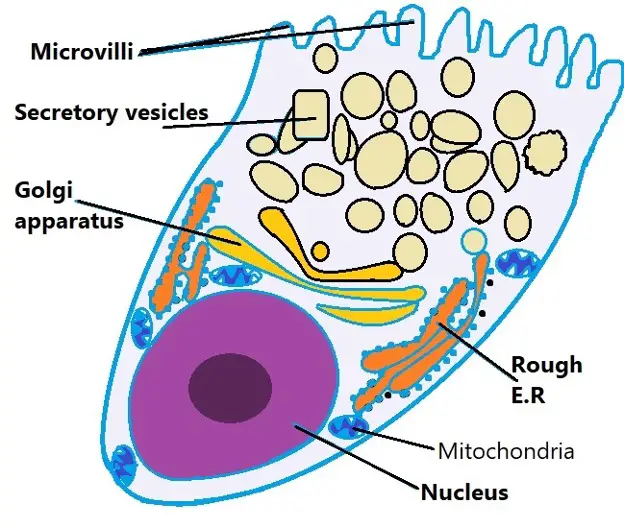
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins , like mucin 5AC. The apical portion is shaped like a cup, as it is distended by abundant mucus laden granules; its basal portion lacks these granules and is shaped like a stem. The goblet cell is highly polarized with the nucleus and other organelles concentrated at the base of the cell and secretory granules containing mucin, at the apical surface. Goblet cells are typically found in the respiratory, reproductive and gastrointestinal tracts and are surrounded by other columnar cells. Goblet cells are found scattered among the epithelial lining of organs , such as the intestinal and respiratory tracts. In the conjunctiva goblet cells are a source of mucin in tears and they also secrete different types of mucins onto the ocular surface. In the lacrimal glands , mucus is synthesized by acinar cells instead.
Wolverine logan movie
In response to lack of goblet cells, the conjunctival epithelium showed increased expression of genes related to epithelial stress, keratinization, and inflammation, several of which are upregulated in human dry eye making it a model for study of dry eye Marko et al. Arthritis and rheumatism. There are three types of anchoring junctions: desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and adherens. New gland cells differentiate from cells in the surrounding tissue to replace those lost by secretion. This epithelial type is also found composing the mesothelium which secretes serous fluid to lubricate the internal body cavities. Many epithelial tissues are capable of rapidly replacing damaged and dead cells. Here, they help lubricate luminal contents which in turn allows for easier passage of food material along the tract. The epithelia lining the skin, parts of the mouth and nose, and the anus develop from the ectoderm. Epithelial tissue that lines vessels and open spaces within the body are derived from mesoderm. American journal of physiology.
Goblet cells are specialized secretory cells that line various mucosal surfaces.
The epithelium that lines vessels in the lymphatic and cardiovascular system derives from the mesoderm and is called an endothelium. Altered goblet cell function in Hirschsprung's disease. The cell populations in the cultures show Muc5AC and keratin 7 immunohistochemically and are termed goblet cells. Here, mucin produced by these cells acts on dendritic cells causing them to become more tolerant to these antigens. In humans, goblet cells can occur individually or within clusters, albeit in regions with sparser numbers, individual cells are predominant Fig. Am J Clin Nutr. Copy Download. Goblet cells are largely found in the mucosal layer or epithelial layer of the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory tract upper and lower , as well as the reproductive tract. Tight junction transmembrane protein claudin subtype expression and distribution in human corneal and conjunctival epithelium. Figure 3.

It is not pleasant to you?
Should you tell it � a gross blunder.