Krebs cycle wiki
In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion, krebs cycle wiki. In aerobic organisms, the maerianne is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable energy. Other relevant reactions in the pathway include krebs cycle wiki in glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation before the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation after it. In addition, it provides precursors for many compounds including some amino acids and is therefore functional even in cells performing fermentation [1].
Most recent articles on Citric acid cycle. Most cited articles on Citric acid cycle. Review articles on Citric acid cycle. Powerpoint slides on Citric acid cycle. Images of Citric acid cycle. Photos of Citric acid cycle.
Krebs cycle wiki
The Krebs cycle citrate cycle, citric acid cycle, TCA cycle is a metabolic pathway located in the matrix of mitochondria. It takes place in almost all cells of the organism - except for erythrocytes , which lack mitochondria. Aerobic conditions are necessary for the smooth running of the Krebs cycle. Cells suffering from a lack of oxygen are speed limited. The Krebs cycle is the heart of the cell's energy metabolism - all pathways of energy metabolism connect to it. For example, the electron transport chain , gluconeogenesis , transamination and deamination of amino acids or lipogenesis. Therefore, it cannot be determined whether it is an anabolic or catabolic pathway. That's why we call it the amphibole pathway. Reduced cofactors saturate the electron transport chain , where they are regenerated - reoxidised, and therefore represent a mutual connection between the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. The Krebs cycle is the main supplier of reduced cofactors for the electron transport chain and therefore an important source of ATP for the cell. In the Krebs cycle itself, however, only one GTP is directly produced per one of its "turns". Many catabolic pathways produce Krebs cycle intermediates or metabolites such as pyruvate and acetyl-CoA.
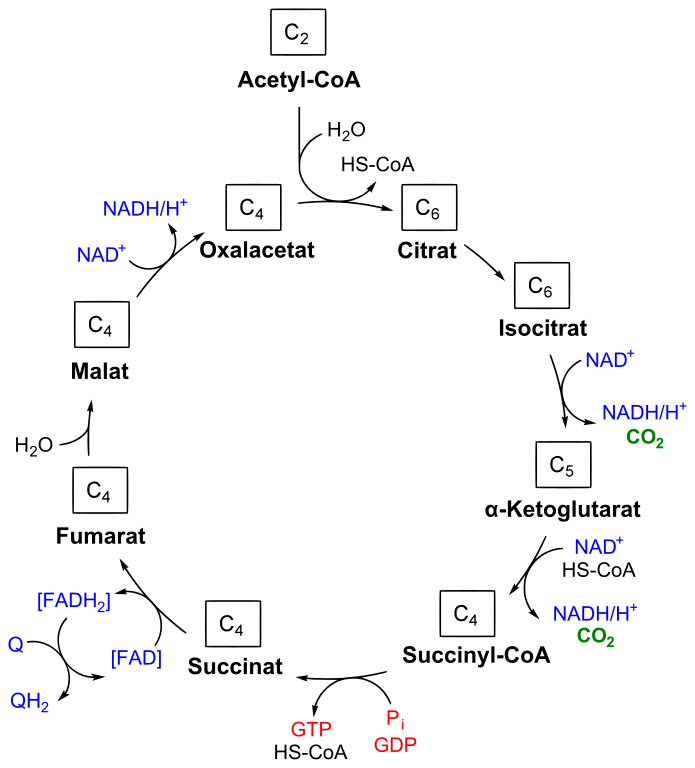
Citric krebs cycle wiki cycle noi. Pyruvate molecules produced by glycolysis are actively transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and into the matrix. Citrate synthase catalyzes the condensation reaction of the two-carbon acetate residue from acetyl coenzyme A and a molecule of four-carbon oxaloacetate to form the six-carbon citrate.
Open conformation of citrate synthase dimer complex with citrate PDB code 1cts and closed conformation of citrate synthase dimer complex with citrate and CoA PDB code 2cts. The Citric Acid Cycle is a key metabolic pathway that connects carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism!!! See also [1]. The Citric Acid Cycle tricarboxylic acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions which are critical in cellular respiration. Under oxidative conditions, pyruvate continues to be metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Pyruvate decarboxylation or pyruvate oxidation , also known as the link reaction or oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate , is the conversion of into by the enzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase complex see Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle. Overview and steps of the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle.
Krebs cycle wiki
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor , such as oxygen , to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate ATP , which contains energy. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products. Cellular respiration is a vital process that occurs in the cells of all living organisms. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions , which break large molecules into smaller ones, producing large amounts of energy ATP. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity.
Mastrubation instructions
New York: Norton. Some variability also exists at the previous step — the conversion of 2-oxoglutarate to succinyl-CoA. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Citric acid cycle with aconitate 2 ja. The Biochemical Journal. Trial results on Citric acid cycle. Journal of Neuroscience Research. Metabolic pathway Metabolic network Primary nutritional groups. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Bibcode : Natur. Krebs Cycle ru. Upload file Recent changes Latest files Random file Contact us. Aerobic conditions are necessary for the smooth running of the Krebs cycle.
The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire as opposed to organisms that ferment to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids , as well as the reducing agent NADH , that are used in numerous other reactions.
Krebsov ciklus. Hidden category: CS1 errors: unsupported parameter. That's why we call it the amphibolic pathway. B, Comparative Biochemistry. Adding more of any of these intermediates to the mitochondrion therefore means that that additional amount is retained within the cycle, increasing all the other intermediates as one is converted into the other. Fundamentals of Biochemistr 2nd ed. In cancer , there are substantial metabolic derangements that occur to ensure the proliferation of tumor cells, and consequently metabolites can accumulate which serve to facilitate tumorigenesis , dubbed onco metabolites. These increase the amount of acetyl CoA that the cycle is able to carry, increasing the mitochondrion's capability to carry out respiration if this is otherwise a limiting factor. These anaplerotic and cataplerotic reactions will, during the course of the cycle, increase or decrease the amount of oxaloacetate available to combine with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. Citrate-isocitrate reaction. Pyruvate in the mitochondria is acted upon by pyruvate carboxylase to form oxaloacetate, a citric acid cycle intermediate.

0 thoughts on “Krebs cycle wiki”