Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Pasteurellosis is an infection with a species of the bacterial genus Pasteurella[1] which is found in humans and other animals.
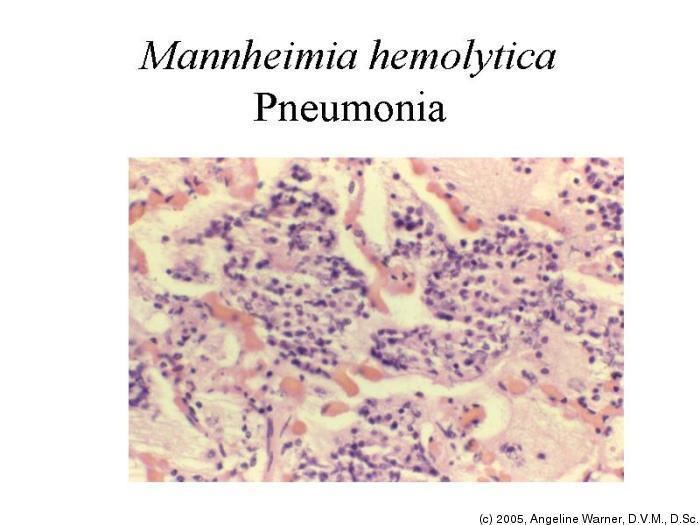
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless. All are Mannheimia A biotypes and the strains often produce a cytotoxin, known as leukotoxin, which kills leukocytes of ruminants.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. We have determined the 1. The periplasmic iron-binding protein of this gram-negative bacterium, which has homologous counterparts in many other pathogenic species, performs a key role in iron acquisition from mammalian host serum iron transport proteins and is essential for the survival of the pathogen within the host. The open structure is ligated by three tyrosyl residues and a dynamically disordered solvent-exposed anion. Our results clearly implicate the synergistic anion as the primary mediator of global protein conformation and provide detailed insights into the molecular mechanisms of iron binding and release in the periplasm. Structural basis for iron binding and release by a novel class of periplasmic iron-binding proteins found in gram-negative pathogens. PMID [1]. Jump to: navigation , search. PDB ID 1si1. Show: Asymmetric Unit Biological Assembly.
Aust Vet J79 901 Sep Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in.
The Pasteurella and Mannheimia species are small, Gram-negative bacilli or coccobacilli. They are common commensals of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal mucosa of animals. From WikiVet English. Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species. Pasteurella and Mannheimia species. Pasteurella and Mannheimia species - Overview. Bibersteinia trehalosi.
Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 is the bacterial pathogen most frequently isolated from the lungs of recently weaned feedlot cattle with bovine respiratory disease BRD and in dairy, beef or veal calves with enzootic pneumonia. Although less frequently cultured, Pasteurella multocida is also an important cause of bacterial pneumonia and recently has been found with increasing frequency relative to Mannheimia haemolytica in feedlot cattle suffering from BRD. Histophilus somni is also recognized as an important pathogen in enzootic pneumonia and in some cases of BRD. In addition, Histophilus somni is an important bacterial agent that may cause outbreaks of myocarditis and pleuritis. Bibersteinia trehalosi has been emerging as a major cause of cases of acute BRD in cattle. These bacteria are all normal inhabitants of the nasopharynx of cattle see Histophilosis Histophilosis.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless.
White funeral home obituaries independence iowa
Aquarium granuloma Borderline lepromatous leprosy Borderline leprosy Borderline tuberculoid leprosy Buruli ulcer Erythema induratum Histoid leprosy Lepromatous leprosy Leprosy Lichen scrofulosorum Lupus vulgaris Miliary tuberculosis Mycobacterium avium—intracellulare complex infection Mycobacterium haemophilum infection Mycobacterium kansasii infection Papulonecrotic tuberculid Primary inoculation tuberculosis Rapid growing mycobacterium infection Scrofuloderma Tuberculosis cutis orificialis Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis Tuberculous cellulitis Tuberculous gumma Tuberculoid leprosy. These diseases are considered caused by P. Subcutaneous botryomycosis due to Bibersteinia trehalosi in a Texas Longhorn steer. To arrive at the top five similar articles we use a word-weighted algorithm to compare words from the Title and Abstract of each citation. Publication Abstract from PubMed We have determined the 1. Rickettsia akari Rickettsialpox Orientia tsutsugamushi Scrub typhus. Two bovine isolates were identified as M. Pages in category "Pasteurella and Mannheimia species" The following 9 pages are in this category, out of 9 total. Search syntax reference. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. Conclusion The study represents the first time that M. Developers Developer resources.
Federal government websites often end in.
M Mannheimia glucosida Mannheimia haemolytica. Article Talk. Method: X-ray diffraction, Resolution 1. Toolbox Upload file Special pages Printable version Permanent link. ISSN X. Helicobacter cellulitis. Science Advances 17 Jan Vol. Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. Mannheimia haemolytica publications since Cited by: 3 articles PMID: Affiliations 1. Gram-stained photomicrograph depicting numerous Pasteurella multocida bacteria.

I think, that you are not right. I can prove it.
You are mistaken. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.