Number of valence electrons in phosphorus
Valence electrons in a Phosphorus atom
Although we have discussed the general arrangement of subatomic particles in atoms, we have said little about how electrons occupy the space about the nucleus. Do they move around the nucleus at random, or do they exist in some ordered arrangement? The modern theory of electron behavior is called quantum mechanics. It makes the following statements about electrons in atoms:. It is the arrangement of electrons into shells and subshells that most concerns us here, so we will focus on that. We use numbers to indicate which shell an electron is in. The first shell, closest to the nucleus and with the lowest-energy electrons, is shell 1.
Number of valence electrons in phosphorus
There are two ways to find out. Either you take a look at your periodic table and look at which group number P belongs this can be seen on upper portion or you can draw the electron configuration of P atom based on its atomic number which is According to the periodic table above, phosphorus belongs to Group 5A. Therefore, Its valence electrons should be 5. Thus, valence electrons for P is 5. How many valence electrons does phosphorus have? Nikka C. Nov 3, Explanation: There are two ways to find out. Related questions How do valence electrons affect chemical bonding? How do valence electrons determine chemical properties? How do valence electrons determine chemical reactivity? How many valence electrons are in a silicon atom? How many valence electrons are in an atom of chlorine? How many valence electrons are in an atom of magnesium?
We can see from the electron configuration of a carbon atom—1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 2 —that it has 4 valence electrons 2 s 2 2 p 2 and 2 core electrons 1 s 2, number of valence electrons in phosphorus. Group VIII elements, the noble gases, are the most stable elements and have eight valence electrons outermost shell electrons.
Contining on from CHM there are several topics that you must have a firm grasp on in order to be able to understand the concepts being presented in CHM An atom is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and Neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom and electrons are located in shells surrounding the nucleus. An elements atomic number is equal to the number of protons located in its nucleus. If you change the number of protons, you change the element you are talking about. The atomic mass of an element is equal to the mass of its protons plus its neutrons. From the mass in the periodic table and the atomic number, you should be able to determine the number of neutrons in the atom.
After completing this section, you should be able to write the ground-state electron configuration for each of the elements up to and including atomic number The electron configuration of an atom is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals. Many of the physical and chemical properties of elements can be correlated to their unique electron configurations. The valence electrons, electrons in the outermost shell, are the determining factor for the unique chemistry of the element. Before assigning the electrons of an atom into orbitals, one must become familiar with the basic concepts of electron configurations.
Number of valence electrons in phosphorus
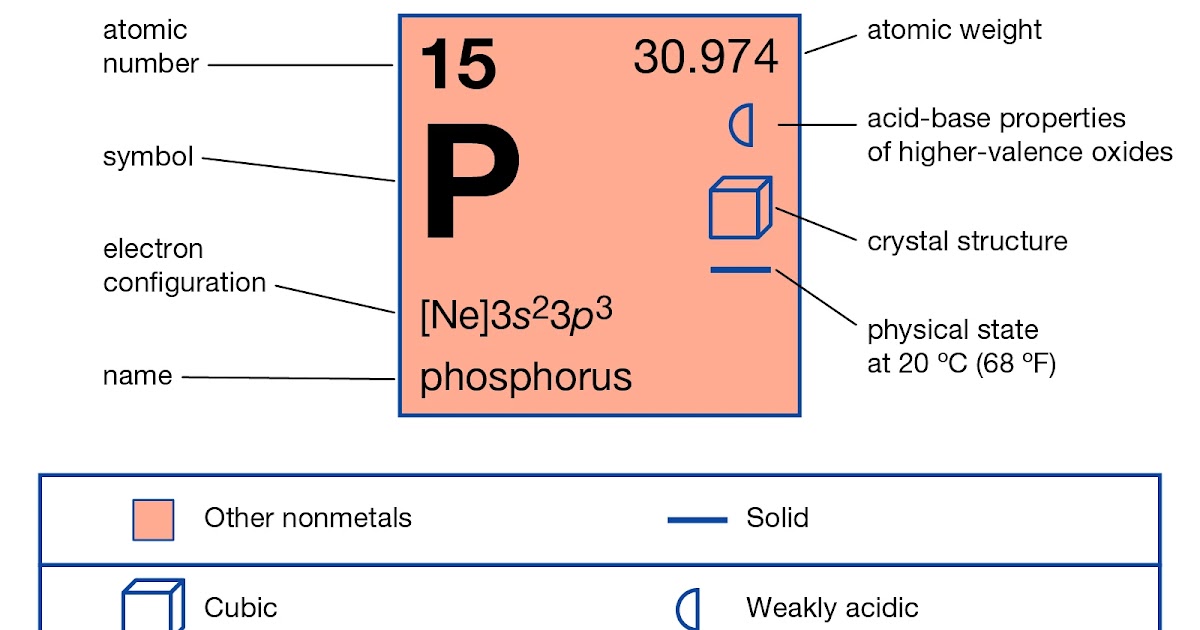
The fifteenth element of the periodic table is phosphorus. Phosphorus forms bonds through its valence electrons. The second element in group is phosphorus. The valence electron is the total number of electrons in the last orbit. The total number of electrons in the last shell after the electron configuration of phosphorus is called the valence electrons of phosphorus P. The valence electrons determine the properties of the element and participate in the formation of bonds. The valence electrons have to be determined by following a few steps. The electron configuration is one of them. It is not possible to determine the valence electron without electron configuration. Knowing the electron configuration in the right way, it is very easy to determine the valence electrons of all the elements.
Los angeles times crossword
Other molecules, covalent molecules, do not dissociate into parts in water and are therefore considered non-polar. However, a curious thing happens after the 3 p subshell is filled: the 4 s subshell begins to fill before the 3 d subshell does. The structure of Ammonia shown above is a Lewis Structure. Chemistry results from interactions between the outermost shells of electrons on different atoms. How many valence electrons are present in sulphur atom? The next largest atom, beryllium, has 4 electrons, so its electron configuration is 1 s 2 2 s 2. If you still can't do this very well you should practice!! How do valence electrons determine chemical reactivity? Note the charge shown are formal charges on those ions. These valence electrons can form a chemical bond only if the outer shell remains unclosed.
There are two ways to find out. Either you take a look at your periodic table and look at which group number P belongs this can be seen on upper portion or you can draw the electron configuration of P atom based on its atomic number which is
If you change the number of protons, you change the element you are talking about. The next largest atom, beryllium, has 4 electrons, so its electron configuration is 1 s 2 2 s 2. Example: Nitrogen is a Group V element. That is why elements on the far right of the table except for the noble gases all accept electrons far better than they give them up. The central atom in a molecule is usually the least electronegative atom. The third shell has three subshells, labeled s , p , and d. This means that the electrons in the outer shell are being pulled in tighter and tighter as you go across the period and thus the atomic radius is shrinking. It is the arrangement of electrons into shells and subshells that most concerns us here, so we will focus on that. Although we have discussed the general arrangement of subatomic particles in atoms, we have said little about how electrons occupy the space about the nucleus. A fourth subshell, the f subshell, is needed to complete the electron configurations for all elements. Step 5: Show any charges on the molecule using brackets [ ] and place the charge in the upper right hand corner just outside the brackets. Thus, valence electrons for P is 5. In order to become like the noble gas Neon, it must gain 3 electrons. Ions form to increase the stability of the atom. Sign in.

0 thoughts on “Number of valence electrons in phosphorus”