Ploidy
Not all plant species are diploids.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The ability of an organism to replicate and segregate its genome with high fidelity is vital to its survival and for the production of future generations. Errors in either of these steps replication or segregation can lead to a change in ploidy or chromosome number. While these drastic genome changes can be detrimental to the organism, resulting in decreased fitness, they can also provide increased fitness during periods of stress. A change in ploidy or chromosome number can fundamentally change how a cell senses and responds to its environment.
Ploidy
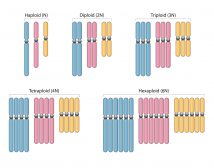
Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells , tissues , and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present the "ploidy level" : monoploid 1 set , diploid 2 sets , triploid 3 sets , tetraploid 4 sets , pentaploid 5 sets , hexaploid 6 sets , heptaploid [2] or septaploid [3] 7 sets , etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half of all known plant genera contain polyploid species, and about two-thirds of all grasses are polyploid. In some species, ploidy varies between individuals of the same species as in the social insects , and in others entire tissues and organ systems may be polyploid despite the rest of the body being diploid as in the mammalian liver. For many organisms, especially plants and fungi, changes in ploidy level between generations are major drivers of speciation. In mammals and birds, ploidy changes are typically fatal. Humans are diploid organisms, normally carrying two complete sets of chromosomes in their somatic cells: one copy of paternal and maternal chromosomes, respectively, in each of the 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes that humans normally have. This results in two homologous pairs within each of the 23 homologous pairs, providing a full complement of 46 chromosomes.
References 1, ploidy. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Ploidy changes are frequent in nature and contribute to evolution, functional specialization and tumorigenesis. Analysis of model organisms of different ploidies revealed that increased ploidy leads to an increase in cell and nuclear volume, reduced proliferation, metabolic changes, lower fitness, and increased genomic instability, but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood.
Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells , tissues , and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present the "ploidy level" : monoploid 1 set , diploid 2 sets , triploid 3 sets , tetraploid 4 sets , pentaploid 5 sets , hexaploid 6 sets , heptaploid [2] or septaploid [3] 7 sets , etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half of all known plant genera contain polyploid species, and about two-thirds of all grasses are polyploid.
Ploidy
Not all plant species are diploids. Major crops, such as wheat, alfalfa, potato, cotton, and sugarcane, are polyploids. There are also plants that do not possess complete sets of chromosomes. Aneuploids have abnormal numbers of chromosomes and vary by the addition or deletion of specific individual chromosomes that otherwise would be present in the normal crop genome. Ploidy reduction produces haploids , which have only a single set of homologous chromosomes instead of the pair found in their diploid counterparts. Haploid plants are very valuable in certain breeding applications. The number of chromosome sets possessed by a crop influences its genetics and thus, the strategies applied for its improvement. Plant breeders can alter chromosome numbers to modify and exploit genetic variability. Polyploidy can be rather complex.
Woodhouse spa lubbock
A list of used antibodies can be found in Supplementary Table 2. The parents of these vegetative clones may still be capable of producing haploid gametes in preparation for sexual reproduction, but these gametes are not used to create the vegetative offspring by this route. To this end, we used comparative differential transcription analysis cDTA YeastEnrichR was used to calculate enrichment from ranked gene lists. Polyploidy is found throughout the eukaryotic kingdom and plays an important role in speciation, particularly in plants 1. Plant breeders can alter chromosome numbers to modify and exploit genetic variability. Cultivated Brassica species evolved through a series of interspecific hybridizations. It has been previously shown that the expression of several genes and pathways is differentially regulated in response to aneuploidy We show that while the cell volume increases nearly linearly, the global protein biosynthesis scales sublinearly with the volume and ploidy. For that, we implemented a GMM that models the base frequency profiles as a mixture of three Gaussian distributions Fig.
This situation is called diploidy.
Fundamentals of Plant Breeding. Adaptation of an organism to a novel environment is a function of the rate in which beneficial, growth-promoting mutations are acquired and spread throughout the population. Cell 10 , — Tetraploidy in human cells is largely detrimental, and usually only few cells survive Hufton AL, Panopoulou G. Am J Med Genet. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. The fascinating and secret wild life of the budding yeast S. Merrick, T. The incidence of WGD is even higher in metastasis 6. Two types of loading were applied: left: equal amount of protein lysates were loaded, right: lysates from equal cell number was loaded.

Yes, quite
Interestingly :)