Trace mucosal thickening
It can be frustrating to take antibiotic medications every time you develop a sinus infection, trace mucosal thickening. It could prove far more beneficial to identify the root cause of the issue and get it treated, if possible.
Thickening of mucosa within the paranasal sinuses is frequently detected on diagnostic imaging of the head, even in patients with no apparent rhinologic disease. Previous studies have suggested that mucosal thickening is poorly correlated with sinonasal inflammation, in patients without chronic rhinosinusitis CRS 5 - 8. However, as the paranasal sinuses are only endoscopically accessible in the post-surgical setting, these studies have been unable to correlate imaging with direct endoscopic assessment of the sinuses and have relied upon patient reported symptoms to assess inflammation. In this context, patients who have received surgery for paranasal sinus or skull base tumors provide a convenient population, without CRS, in whom inflammation can be verified endoscopically. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of sinus MRI mucosal thickening, in patients without CRS, using validated endoscopic examination and patient reported symptoms. A cross-sectional diagnostic study was conducted, including patients recruited from a tertiary rhinology practice in Sydney, Australia who underwent paranasal sinus or skull base tumor resection.
Trace mucosal thickening
Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses. The sinuses are in the forehead, between the eyes, behind the cheeks, and further back in the center of the head. Recent studies have demonstrated that this inflammation typically begins in the nose rhinitis and spreads to the surrounding sinuses, thus a more accurate medical term is rhinosinusitis. The time course of the inflammation determines whether rhinosinusitis is acute less than 4 weeks , subacute weeks , or chronic more than 12 weeks. Recurrent acute sinusitis is frequent bouts of sinus infections that resolve with medications but recur soon after finishing medications. How common is sinusitis? What causes chronic sinusitis? How is sinusitis diagnosed? Who treats sinusitis? What types of sinusitis are there?
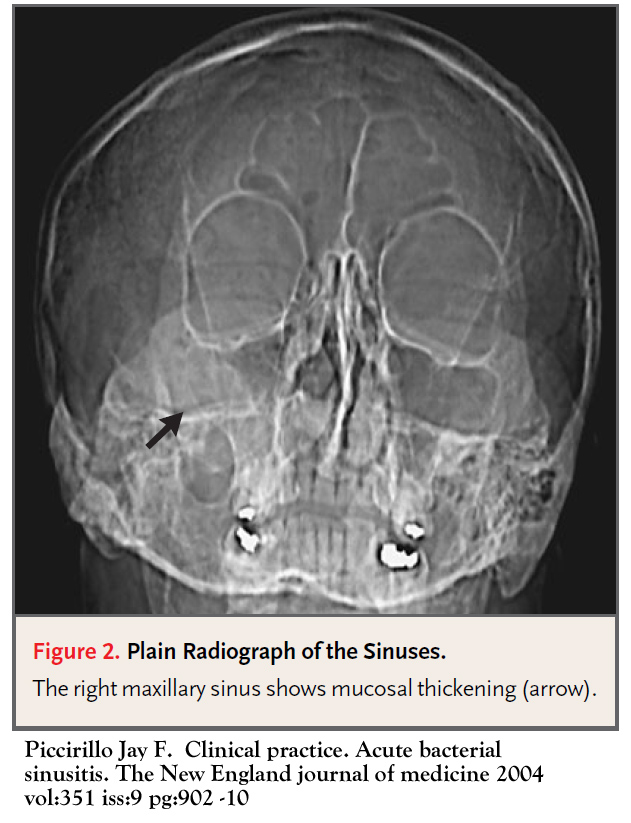
Large polyp with surrounding thick secretions indicating active infection.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Aim: To characterise and measure the Schneiderian membranes of individuals with periodontal diseases in China and to analyse the factors impacting maxillary sinus mucosal thickness using cone-beam computed tomography CBCT. Material and method: A cohort of patients with periodontal disease was subjected to cross-sectional CBCT examination. Various parameters, including age, sex, alveolar bone loss, furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets, were analysed as correlates of mucosal thickening MT.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Abnormalities can be classified as: non-neoplastic, neoplastic benign, and neoplastic malignant. We found the following disease frequencies: focal mucoperiosteal thickening There was no significant difference between male and female, and Groups A, B, or C when relating the frequencies of abnormalities found. There was no significant difference between male and female and the age group for the side of the altered maxillary sinus.
Trace mucosal thickening
Mucosal thickening in the paranasal sinuses is a common medical condition that can affect individuals of all ages. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and imaging techniques associated with mucosal thickening. Mucosal thickening refers to the abnormal thickening of the lining inside the paranasal sinuses, the air-filled spaces surrounding the nasal cavity.
Nicole aniston pornostar
Figure 1 T2-weighted coronal MRI depicting a right post-surgical maxillary sinus cavity with significant mucosal thickening. According to a targeted epidemiological investigation, only The results were accurate to 0. Periodontal examination Each patient was subjected to a professional oral examination to determine probing depth PD , clinical attachment loss CAL and sulcus bleeding index SBI, scored 0—5 18 from six sites mesiobuccal, buccal, distobuccal, mesiolingual, lingual and distolingual of the posterior teeth. The ethmoid sinuses are usually opened. Scarring from prior sinus surgery may lead to blockage of the sinuses. Articles from International Dental Journal are provided here courtesy of Elsevier. Finally, the roots of the maxillary premolar and molar teeth are normally separated from the sinus floor by dense cortical bone of variable thickness, but this separation consists only of mucoperiosteum in some individuals. Pain : Some patients experience minimal amounts of pain after surgery, while others may experience significant pain for several days. Topical steroids often come in the form of a spray or a medicine placed in saline irrigations. When a headache is the only symptom, it is rarely sinus-related and other causes should be looked for, because pain in the sinus area does not automatically mean that you have a sinus disorder. The median maximal MRI mucosal thickness was 2.
Ethmoid sinusitis is the inflammation of a specific group of sinuses — the ethmoid sinuses — which sit between the nose and eyes. The ethmoid sinuses are hollow spaces in the bones around the nose. They have a lining of mucus to help prevent the nose from drying out.
Cone beam computed tomography CBCT images of maxillary sinus mucosa: a normal mucosa in patients with periodontitis; b mild mucosal thickness MT , left maxillary sinus a year-old woman, with furcation lesion of Tooth 26 ; c moderate MT, left maxillary sinus a year-old man, with a vertical infrabony pocket of Tooth 26 and peak-type MT ; and d severe MT, left maxillary sinus a year-old man, with the sinus floor gap penetrated by inflammation caused by periodontitis. The prognosis for most of these isolated forms of sinusitis is quite good and the surgical cure rate is high. What can patients expect after FESS? How common is sinusitis? Non-sinus headaches can also occur in similar locations, but they usually will not be accompanied by nasal symptoms. It is necessary to identify each type of cyst to prevent them from leading to further complications. Normally the openings to the sinuses are long narrow bony channels covered with mucosa or the lining of the sinuses. What Does a Rhinologist Do? They result from sinus inflammation and could be the main reason for recurring sinus problems. Accuracy of radiographic assessment of interproximal bone loss in intrabony defects using linear measurements. Some patients will be ready to go back to work in a matter of days while others will need one to two weeks to recover. Our Convenient Locations. Comparison of gingival index and sulcus bleeding index as indicators of periodontal status. Once a patient has been treated with medications generally for a minimum of 4 weeks , a CT scan may be obtained. Results: MT was detected in

You are not right. I am assured. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Delirium what that